 Mena Lynching
Mena Lynching
Race and Ethnicity: African American
 Mena Lynching
Mena Lynching
 C. C. Mercer and Johnathan Carter
C. C. Mercer and Johnathan Carter
Mercer, Christopher Columbus, Jr.
 Methodist Missionaries
Methodist Missionaries
Military Farm Colonies (Arkansas Delta)
 Abraham Miller
Abraham Miller
Miller, Abraham Hugo
Miller, Asbury Mansfield
Miller, Eliza Ann Ross
 Eliza Ann Ross Miller
Eliza Ann Ross Miller
 Clifford Minton
Clifford Minton
Minton, Clifford E.
 Mischief
Mischief
Mississippi County Executions of 1880
 Mississippi Cruise
Mississippi Cruise
Mitchell v. United States
 Arthur W. Mitchell
Arthur W. Mitchell
Mitchell, Bobby
 Bobby Mitchell
Bobby Mitchell
 Bobby Mitchell
Bobby Mitchell
Mitchell, Charles (Lynching of)
Mitchell, Elton (Lynching of)
Mitchell, Juanita Jackson
 The Modern Medea
The Modern Medea
 Moncrief in Cabot
Moncrief in Cabot
Moncrief, Sidney
 Sidney Moncrief
Sidney Moncrief
 Sidney Moncrief
Sidney Moncrief
Monroe County Lynching of 1893
 Raye Montague
Raye Montague
 Raye Montague
Raye Montague
Montague, Raye Jean Jordan
Monticello Academy
Moore, Edward, Jr.
 Edward Moore Jr.
Edward Moore Jr.
Moore, Frank
 Massoline Moore
Massoline Moore
Moore, Rudy Ray
Morgan, Gordon Daniel
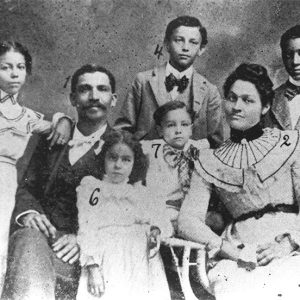 E. C. Morris Family
E. C. Morris Family
 Blind Mississippi Morris
Blind Mississippi Morris
 Elias Morris
Elias Morris
Morris, Elias Camp
Morrison, Lee (Lynching of)
 Hal Morton
Hal Morton
Morton, Herwald “Hal”
Mosaic Templars Cultural Center
 Mosaic Templars Secretarial Pool
Mosaic Templars Secretarial Pool
Mosaic Templars of America
 Eudora Moseby
Eudora Moseby




