 Freund Print
Freund Print
Entry Type: Thing
 Freund Print
Freund Print
 Freund Necklace
Freund Necklace
 Freund Mural
Freund Mural
Fried Dill Pickles
 Fryers Ford Bridge
Fryers Ford Bridge
Fulbright Industries
Fulbright Memorandum
 Fulbright Sketch
Fulbright Sketch
 Fulbright Statue
Fulbright Statue
 Fuligo septica
Fuligo septica
Fuller-Shannon House
 Fulton Ferry
Fulton Ferry
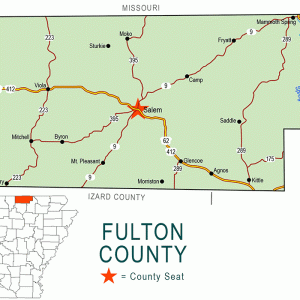 Fulton County Map
Fulton County Map
Funeral Customs, Traditional (Ozark Mountains)
Fungi
G. A. Thompson [Steamboat]
Gaines House
Galatia Church
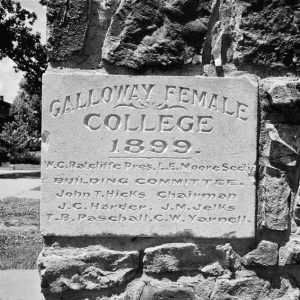 Galloway Female College Marker
Galloway Female College Marker
Galloway Women’s College
aka: Galloway Female College
 Gallows
Gallows
Gambling (Legal)
Gann House
 Gann Museum
Gann Museum
 Gant Drawing
Gant Drawing
 GAR Application
GAR Application
 GAR Monument
GAR Monument
 GAR Monument, Siloam Springs
GAR Monument, Siloam Springs
 GAR Monument Inscription
GAR Monument Inscription
Garage Bands
Garland County Courthouse
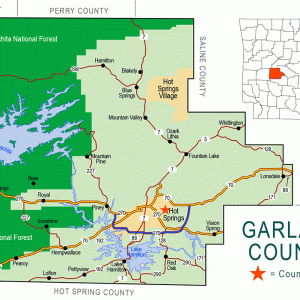 Garland County Map
Garland County Map
Garland County Public Library
Garrett Whiteside Hall
Gars
aka: Garfish
aka: Garpikes
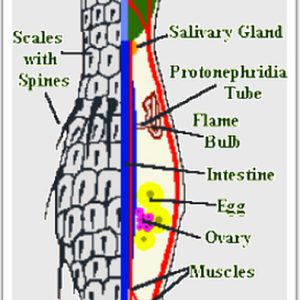 Gastrotrich Morphology
Gastrotrich Morphology
Gastrotrichs
aka: Hairybacks
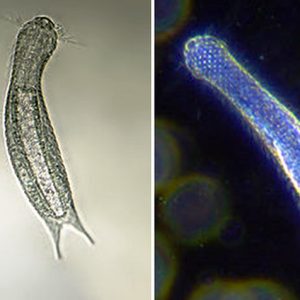 Gastrotrichs
Gastrotrichs
 The Gatekeepers by Pat Musick
The Gatekeepers by Pat Musick
Gatewood House
Gay Oil Company Building
Geckos
 Geckos
Geckos
General Bem [Steamboat]
General Improvement Fund
General Robert E. Lee Monument
 General Robert E. Lee Monument
General Robert E. Lee Monument
 General Robert E. Lee Monument
General Robert E. Lee Monument
 General Robert E. Lee Monument
General Robert E. Lee Monument
 General Robert E. Lee Monument
General Robert E. Lee Monument




