Entry Type: Thing
 Gentry GAR Monument
Gentry GAR Monument
 Geocarpon Minimum
Geocarpon Minimum
Geographical Center of Arkansas Marker
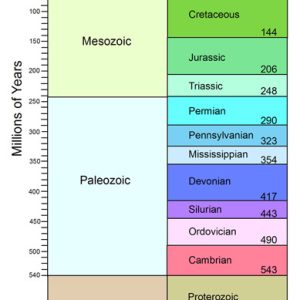 Geologic Time Scale
Geologic Time Scale
Geophagy
aka: Geophagia
aka: Pica
George Berry Washington Memorial
 Green Elf Court Ad
Green Elf Court Ad
George W. Mallett House
German National Bank
 GFWC Sticker
GFWC Sticker
Ghost Legends
 Giant Swallowtail Butterfly
Giant Swallowtail Butterfly
Gibson Baskets
 Gibson Hamper
Gibson Hamper
 Gibson Road—Fourth Street
Gibson Road—Fourth Street
 Gibson Turkey Box
Gibson Turkey Box
 Gibson Turkey Box
Gibson Turkey Box
Gillham City Jail
Girl Scouts
Girls Domestic Science and Arts Building (Arkansas Tech University)
aka: Old Art Building (Arkansas Tech University)
aka: Browning Hall (Arkansas Tech University)
Glasgow Affair
Glenwood Iron Mountain Railroad Depot
 Glosson and Raney Ad
Glosson and Raney Ad
God’s Not Dead 2
 God's Not Dead 2
God's Not Dead 2
 God's Not Dead 2 Poster
God's Not Dead 2 Poster
God’s Not Dead: A Light in Darkness
 Goddess of Liberty
Goddess of Liberty
 Gold Mine Springs Mines
Gold Mine Springs Mines
Gold Mine Springs Mines
Goldeyes and Mooneyes
aka: Mooneyes and Goldeyes
aka: Hiodontid Fishes
 Goldeyes and Mooneyes
Goldeyes and Mooneyes
Golf
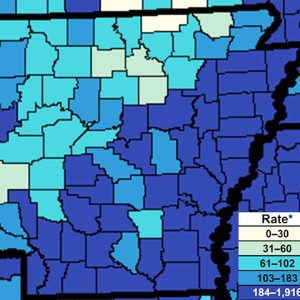 Gonorrhea in Arkansas
Gonorrhea in Arkansas
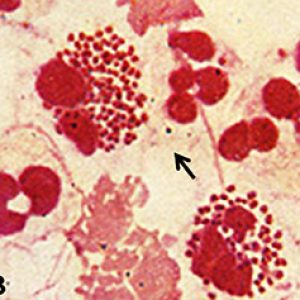 Gonorrhea Morphology
Gonorrhea Morphology
Goodlett Gin
 Goodlett Steam-Powered Cotton Gin
Goodlett Steam-Powered Cotton Gin
Goodspeed Histories
 Gosnell Vietnam War Monument
Gosnell Vietnam War Monument
Gospel Music
Gospel of Eureka, The
Government Free Bathhouse
Governor, Office of the
Gowrow
 Gowrow Article
Gowrow Article
Grand Army of the Republic Monument (Gentry)
Grand Army of the Republic Monument (Judsonia)
Grand Army of the Republic Monument (Siloam Springs)
 Grand Canyon View
Grand Canyon View




