Entry Type: Thing - Starting with L
L’Anguille River
Labor Movement
Laconia Circle Levee
 Laconia Circle Levee Monument
Laconia Circle Levee Monument
Lady Baxter
 "Lady Baxter"
"Lady Baxter"
Lafayette County Courthouse
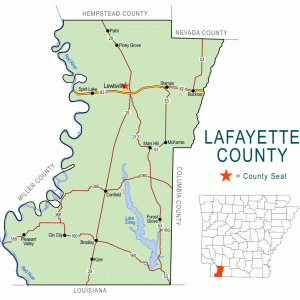 Lafayette County Map
Lafayette County Map
Lafayette Hotel
aka: Lafayette Building
 Lafayette Hotel Remodel
Lafayette Hotel Remodel
 Lafayette Hotel Key
Lafayette Hotel Key
 Lake Catherine Power Station
Lake Catherine Power Station
Lake Catherine State Park Prisoner of War Structures
Lake Chicot
Lake Conway Monster
aka: Skunk Ape
Lake Nixon
 Lake Nixon
Lake Nixon
Lake Norrell
 Lake Trout
Lake Trout
Lake Village Confederate Monument
 Lake Village Confederate Soldiers Monument
Lake Village Confederate Soldiers Monument
Lake Village Post Office
Lake Winona
aka: Alum Fork Reservoir
Lakes
Lamar Porter Athletic Field
Lampreys
aka: Jawless Fishes
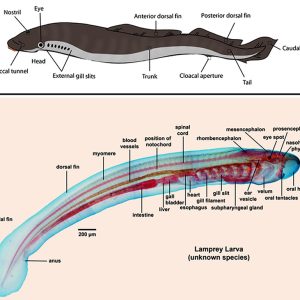 Lamprey Comparative Morphology
Lamprey Comparative Morphology
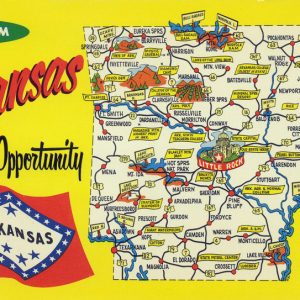 "Land of Opportunity" Postcard
"Land of Opportunity" Postcard
Landlord-Tenant Laws
 Large Catfishes of Arkansas
Large Catfishes of Arkansas
Large Standing Figure: Knife Edge
aka: Standing Knife [Sculpture]
 Large Standing Figure: Knife Edge
Large Standing Figure: Knife Edge
 Large Standing Figure: Knife Edge
Large Standing Figure: Knife Edge
 Bob Larkan Record
Bob Larkan Record
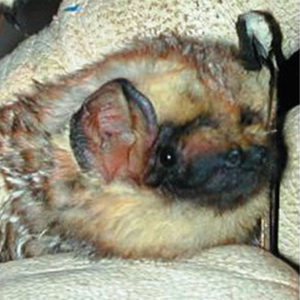 Lasiurus Bats
Lasiurus Bats
Lassis Inn
 "Last Date," Performed by Floyd Cramer
"Last Date," Performed by Floyd Cramer
 The Last Days by Cicero Pilgrim
The Last Days by Cicero Pilgrim
 Last Lick of Summer
Last Lick of Summer
 Last Passenger Pigeon
Last Passenger Pigeon
 The Last Ride
The Last Ride
 Late Breakfast
Late Breakfast
Latimore Tourist Home
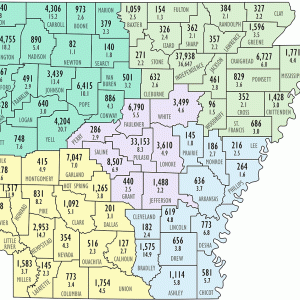 Latino Population Map
Latino Population Map
Lavacaberry
 Lavacaberry Crate Label
Lavacaberry Crate Label
Lawrence County Courthouse
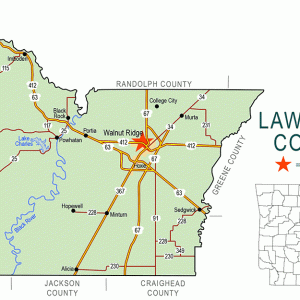 Lawrence County Map
Lawrence County Map




