Entry Type: Thing
 Fort Smith Free Bridge
Fort Smith Free Bridge
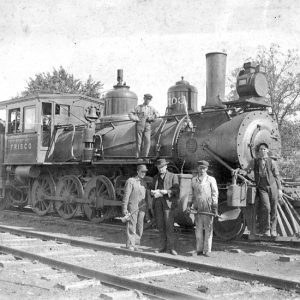 Fort Smith Locomotive
Fort Smith Locomotive
Fort Smith Museum of History
Fort Smith Regional Airport
Fort Smith to Jackson Road
 Fort Towson Trail Marker
Fort Towson Trail Marker
Fort Wayne
Forts Lookout and Southerland
aka: Forts Southerland and Lookout
aka: Fort Diamond
 Fort Southerland
Fort Southerland
 Fort Southerland Park
Fort Southerland Park
 Fort Lookout
Fort Lookout
 Fort Lookout Entrenchment
Fort Lookout Entrenchment
 "Forty Days," Performed by Ronnie Hawkins
"Forty Days," Performed by Ronnie Hawkins
Forty Days and Forty Nights
 Forty-Three Years for Uncle Sam
Forty-Three Years for Uncle Sam
 Fossilized Bryozoans
Fossilized Bryozoans
Fossils
 Foster Band Shell
Foster Band Shell
 Foster Memorial
Foster Memorial
 Foster Memorial Highway
Foster Memorial Highway
 Fouke Bank
Fouke Bank
 Fouke Depot
Fouke Depot
Fouke Monster
 Fourche La Fave Bridge
Fourche La Fave Bridge
 Fourche La Fave River
Fourche La Fave River
Fourche La Fave River
Fourche Mountain Salamander
aka: Plethodon fourchensis
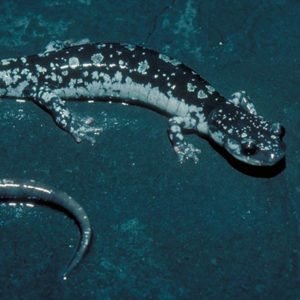 Fourche Mountain Salamander
Fourche Mountain Salamander
 Fourche Mountain Salamander
Fourche Mountain Salamander
 Fourche Mountain Salamander
Fourche Mountain Salamander
 Foushee Cave Snail
Foushee Cave Snail
Fowler Cemetery
Fowler House
aka: Absalom Fowler House
 Fractured Millstone by Robyn Horn
Fractured Millstone by Robyn Horn
Franke’s Cafeteria
Franklin County Courthouse, Northern District
Franklin County Courthouse, Southern District
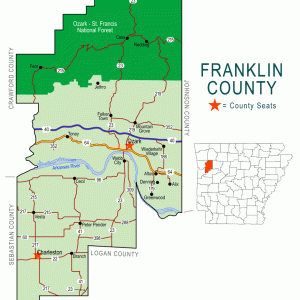 Franklin County Map
Franklin County Map
 Free Bridge
Free Bridge
 Free Bridge
Free Bridge
Freedom Centers, Houses, Schools, and Libraries
 Freedom Riders Plaque
Freedom Riders Plaque
Freedom Suits
 Freemason Monument
Freemason Monument
Frenchman’s Mountain Methodist Episcopal Church and Cemetery
aka: Cato United Methodist Church and Cemetery
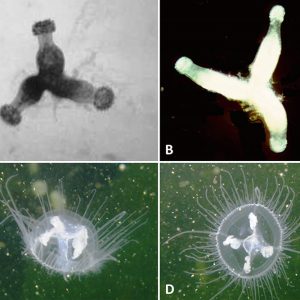 Freshwater Cnidarians
Freshwater Cnidarians
 Freshwater Drum
Freshwater Drum
Freshwater Drum
aka: Grunter
aka: Gaspergou
 Freshwater Isopods
Freshwater Isopods




