 Fisher Coiled Pot
Fisher Coiled Pot
Entry Type: Thing
 Fisher Coiled Pot
Fisher Coiled Pot
 Rosemary Fisher Hallmark
Rosemary Fisher Hallmark
 Fisher Vase
Fisher Vase
 George Fisher WWII Cartoons
George Fisher WWII Cartoons
 Fishing (Anglers II) by Carroll Cloar
Fishing (Anglers II) by Carroll Cloar
Fitzgerald Station and Farmstead
Fitzhugh Snapp Company
 Flag by John Salvest
Flag by John Salvest
 Flag Modification Resolution
Flag Modification Resolution
Flanagin Law Office
Fleas
 Flea Species
Flea Species
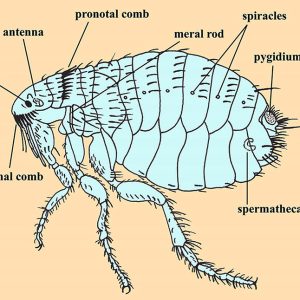 Flea Species
Flea Species
 Flies
Flies
 Flight From Servitude by Les Christensen
Flight From Servitude by Les Christensen
Flint Creek Power Plant
Floating CCC Camp at Jacks Bay
Floods
Florence Crittenton Home
Florida Brothers Building
 Florida Panther
Florida Panther
Fly-fishing
 Fly's Eye Dome
Fly's Eye Dome
 "Flying Saucers Rock 'n Roll"
"Flying Saucers Rock 'n Roll"
 Fogleman Gin
Fogleman Gin
Folk Music
 "Folsom Prison Blues," Performed by Johnny Cash
"Folsom Prison Blues," Performed by Johnny Cash
Food and Foodways
 Foot Lathe
Foot Lathe
 Fordyce House
Fordyce House
 Fordyce House
Fordyce House
 Fordyce House
Fordyce House
 Fordyce House
Fordyce House
Fordyce House
Forest Fire Lookouts
aka: Fire Towers
Forest Management and Conservation
Forest Rose [Steamboat]
Forgotten Girls, The
Forrest L. Wood Crowley’s Ridge Nature Center
Fort Bussey
 Fort Chaffee Drawing
Fort Chaffee Drawing
 Fort Chaffee Drawing
Fort Chaffee Drawing
 Fort Chaffee Newspaper
Fort Chaffee Newspaper
 Fort Curtis Cannon
Fort Curtis Cannon
Fort Hindman
Fort Lincoln
aka: DeValls Bluff Fortifications
 Fort Smith Trolley
Fort Smith Trolley
 Fort Smith in 1836
Fort Smith in 1836
 Fort Smith Confederate Monument
Fort Smith Confederate Monument
 Fort Smith Confederate Monument Base
Fort Smith Confederate Monument Base




