Entry Category: Water
 Arkadelphia City Story
Arkadelphia City Story
 Arkansas City Ferry
Arkansas City Ferry
Arkansas Inland Maritime Museum
Arkansas River
Arkansas Traveler [Steamboat]
 Arkansas Traveler Steamboat Article
Arkansas Traveler Steamboat Article
Arkansas Waterways Commission
Arkansas, Steamboats Named
 Augusta Bridge
Augusta Bridge
B. M. Runyan [Steamboat]
 Barge
Barge
Baring Cross Bridge
 Baring Cross Bridge
Baring Cross Bridge
Bart Tully [Steamboat]
 Bart Tully Article
Bart Tully Article
 Bart Tully Article
Bart Tully Article
 Beaver Bridge
Beaver Bridge
 Before Norfork Lake
Before Norfork Lake
Belle Zane [Steamboat]
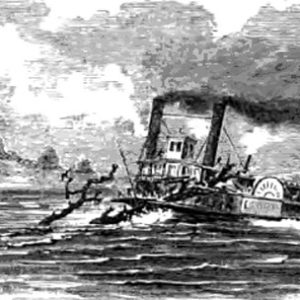 Belle Zane Steamboat
Belle Zane Steamboat
 Benton Bridge
Benton Bridge
Blakely Mountain Dam
aka: Blakely Dam
aka: Lake Ouachita
 Blakely Mountain Dam
Blakely Mountain Dam
 Blakely Mountain Dam
Blakely Mountain Dam
 Blansett Bridge
Blansett Bridge
Brandywine [Steamboat]
 Bridge 178
Bridge 178
Bridges
 Buffalo River Bridge
Buffalo River Bridge
Bull Shoals Dam and Lake
 Bull Shoals Dam Power Plants
Bull Shoals Dam Power Plants
Cache River
 Cache River Bridge
Cache River Bridge
Caddo River
 Calion Bridge
Calion Bridge
Cambridge [Steamboat]
 Cambridge Steamboat Article
Cambridge Steamboat Article
Car of Commerce [Steamboat]
 Car of Commerce Steamboat Article
Car of Commerce Steamboat Article
Caroline [Steamboat]
 Caroline Steamboat Article
Caroline Steamboat Article
 Caroline Steamboat Article
Caroline Steamboat Article
Carpenter Dam
aka: Lake Hamilton
Carpenter, Flavius Josephus (Flave)
 Cedar Creek Bridge
Cedar Creek Bridge
Cherokee [Steamboat]
 Cherokee Steamboat Ad
Cherokee Steamboat Ad
 Cherokee Steamboat Article
Cherokee Steamboat Article
 Chester Bridge
Chester Bridge




