 C. G. "Crip" Hall
C. G. "Crip" Hall
Time Period: Early Twentieth Century (1901 - 1940)
 C. G. "Crip" Hall
C. G. "Crip" Hall
Hallelujah
Hallock, Harry M.
 John Hallum Death
John Hallum Death
 Hamburg Church
Hamburg Church
Hamm, Eddie
 Eddie Hamm
Eddie Hamm
 Hammond Packing Company Story
Hammond Packing Company Story
 Hammond Packing Company Story
Hammond Packing Company Story
Hammond Packing Company v. Arkansas
Hampson, James Kelly
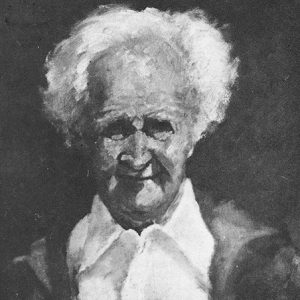 James Kelly Hampson
James Kelly Hampson
 Hampton Waterworks
Hampton Waterworks
Hampton Waterworks
Hancock, James Carl
 Handle Factory
Handle Factory
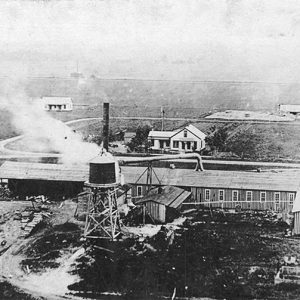 Handle Factory
Handle Factory
 Handy Steamboat
Handy Steamboat
Hanger Hill Historic District
 Frances Hanger
Frances Hanger
Hanger, Frances Marion Harrow
 Hanks Death Notice
Hanks Death Notice
Happy Hollow
aka: McLeod's Amusement Park
 Happy Hollow
Happy Hollow
 Happy Hollow
Happy Hollow
 Happy Hollow Motel
Happy Hollow Motel
 Happy Hollow Postcard
Happy Hollow Postcard
 Happy Hollow Staged Bear Hunt
Happy Hollow Staged Bear Hunt
 Happy Hollow Tourists
Happy Hollow Tourists
 Benjamin Hardin Grave
Benjamin Hardin Grave
 Harding University
Harding University
 Arthur Harding Cadet Medal
Arthur Harding Cadet Medal
Harding, Arthur McCracken
 James Harding
James Harding
 T. W. Hardison
T. W. Hardison
Hardison, T. W.
 Hardy Overlook
Hardy Overlook
 Hardy, View From River
Hardy, View From River
Harper, John (Execution of)
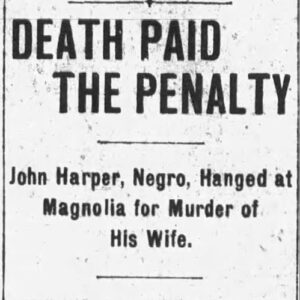 John Harper Execution Story
John Harper Execution Story
Harrington, M. R.
aka: Mark Raymond Harrington
 Harris Family
Harris Family
 Harris Lynching
Harris Lynching
Harris, Gilbert (Lynching of)
 Harris Lynching Article
Harris Lynching Article
Harris, Jack (Lynching of)
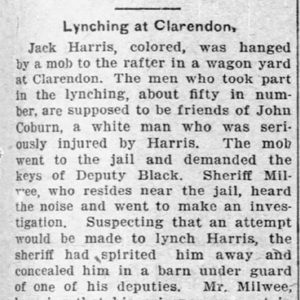 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article




