 R-Pep Label
R-Pep Label
Time Period: Early Twentieth Century (1901 - 1940) - Starting with R
 R-Pep Label
R-Pep Label
Rabbit Foot Lodge
Rabies
Ragon, Hiram Heartsill
 Railroad at Genoa
Railroad at Genoa
 Railroad at Guion Sand Mine
Railroad at Guion Sand Mine
 Railroad Development
Railroad Development
 Railroad Tunnel
Railroad Tunnel
 Railroad Workers
Railroad Workers
 Railroad Workers near Jonesboro
Railroad Workers near Jonesboro
 Railway at Penters Bluff
Railway at Penters Bluff
 Ramsey's Ferry
Ramsey's Ferry
Randolph County Courthouse
 Randolph Hotel
Randolph Hotel
 Randolph Plaque
Randolph Plaque
Randolph, Vance
 Vance Randolph
Vance Randolph
 Vance Randolph
Vance Randolph
 Vance Randolph
Vance Randolph
 Wayne Raney Songbook
Wayne Raney Songbook
Raney, Wayne
 Wayne Raney Sheet Music
Wayne Raney Sheet Music
 Ravenden Springs Cotton
Ravenden Springs Cotton
 Ravenden Springs Logging
Ravenden Springs Logging
 Ravenden Springs View
Ravenden Springs View
 Rawleigh Remedies
Rawleigh Remedies
Ray Winder Field
Ray, Mary Lee McCrary
Rayburn, Otto Ernest
 Razorback Hunters
Razorback Hunters
 Razorback Stadium Dedication
Razorback Stadium Dedication
 Read House
Read House
Read, Lessie Stringfellow
 Lessie Stringfellow Read Article
Lessie Stringfellow Read Article
 Rector Cotton
Rector Cotton
 Rector Depot
Rector Depot
 Rector Drug Store
Rector Drug Store
 Rector Street Scene
Rector Street Scene
 James Rector
James Rector
Rector, James Alcorn “Indian”
 Red Cross Ambulance
Red Cross Ambulance
 Red Cross at Elaine
Red Cross at Elaine
 Red Cross Band
Red Cross Band
 Red Cross Canteen at Elaine
Red Cross Canteen at Elaine
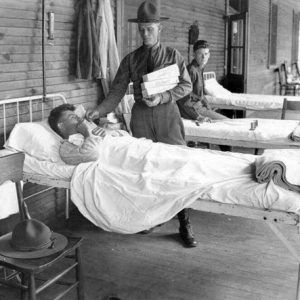 Red Cross Gifts
Red Cross Gifts
 Red Cross HQ
Red Cross HQ
 Red Cross Volunteers
Red Cross Volunteers
 Red River Bridge
Red River Bridge
Red Scare (1919–1920)
aka: First Red Scare
 Red Star Lumber
Red Star Lumber




