Entry Type: Thing - Starting with C
 Conway County Library
Conway County Library
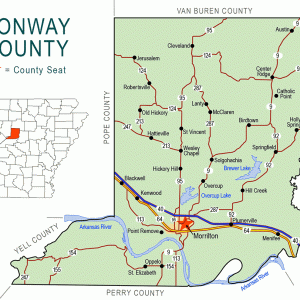 Conway County Map
Conway County Map
 Elias Conway Grave
Elias Conway Grave
Conway Regional Health System
 Cook Cotton Mill
Cook Cotton Mill
Cook-Morrow House
 Cook's Landing
Cook's Landing
Coolidge House
Coop Creek Bridge
 Coop Creek Bridge
Coop Creek Bridge
 Coral Snake & Mimics
Coral Snake & Mimics
 Corinth Sawmill
Corinth Sawmill
 Corning Grain Silos
Corning Grain Silos
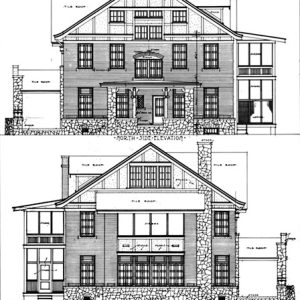 Cornish House Plans
Cornish House Plans
 Ed Cornish Tombstone
Ed Cornish Tombstone
Cornish House
Coronado Coal Co. v. United Mine Workers of America
aka: United Mine Workers of America v. Coronado Coal Co.
Cossatot Community College of the University of Arkansas (CCCUA)
Cossatot River
 Cossatot River Bridge
Cossatot River Bridge
Cotham’s Mercantile
 Cotter Bridge
Cotter Bridge
 Cotter Bridge
Cotter Bridge
 Cotter Bridge
Cotter Bridge
 Cotter Bridge Construction
Cotter Bridge Construction
 Cotter Bridge Construction
Cotter Bridge Construction
Cotter Bridge
aka: R. M. Ruthven Bridge
Cotter Water Tower
 Cotter Water Tower
Cotter Water Tower
Cotton Belt Railroad Depot
 Cotton Belt Railroad Engine
Cotton Belt Railroad Engine
 Cotton Boll Weevil
Cotton Boll Weevil
 Cotton Farm
Cotton Farm
Cotton Gins
Cotton in My Sack
Cotton Industry
 Cotton Seed
Cotton Seed
 Cotton Plant Water Tower
Cotton Plant Water Tower
Cotton Plant Water Tower
 Cotton States League Memo
Cotton States League Memo
 Cottonseed Oil Mill
Cottonseed Oil Mill
 Cottonwood Borer
Cottonwood Borer
 Cottonwood Tree
Cottonwood Tree
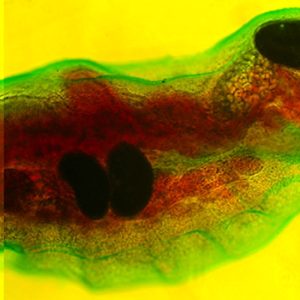 Cotylaspis insignis
Cotylaspis insignis
Couch-Marshall House
 Cougar
Cougar
 Council Oaks Tree
Council Oaks Tree




