Entry Type: Thing - Starting with C
aka: Springtails
Collier Springs Shelter
 Collier Springs Shelter
Collier Springs Shelter
Collins v. State
 Richard Collins Gravesite
Richard Collins Gravesite
Colored Industrial Institute
 Colored Regiments Recruitment Poster
Colored Regiments Recruitment Poster
Columbia County Courthouse
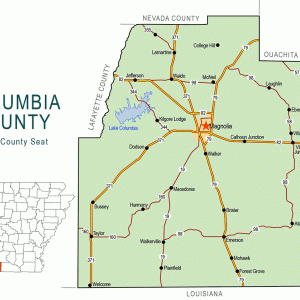 Columbia County Map
Columbia County Map
Combs, Cass and Eastern Railroad
Come Early Morning
Come Next Spring
 Come Next Spring Ad
Come Next Spring Ad
Comet [Steamboat]
Command and Control
Command-Aire
 Command-Aire
Command-Aire
 Command-Aire 5C3-C
Command-Aire 5C3-C
Commercial [Steamboat]
 Commercial National Bank Flyer Featuring Frank White
Commercial National Bank Flyer Featuring Frank White
Commissioner of State Lands, Office of
aka: Office of Land Commissioner
 Community Center Commemorative Plaque
Community Center Commemorative Plaque
Community Mental Health Centers
 Company Locomotive
Company Locomotive
 Compton Lookout
Compton Lookout
 Concatenated Order of Hoo-Hoo Constitution
Concatenated Order of Hoo-Hoo Constitution
 Concatenated Order of Hoo-Hoo Membership Card
Concatenated Order of Hoo-Hoo Membership Card
 Concentric Circles at 3CN17
Concentric Circles at 3CN17
 Cone Trophy
Cone Trophy
 John Cone House
John Cone House
Confederate Battle Flags
 Confederate Monument Postcard
Confederate Monument Postcard
 Confederate Soldiers Monument Inscription
Confederate Soldiers Monument Inscription
Confederate Soldiers Monument
aka: "Defending the Flag," Arkansas Sons of the Confederacy Memorial
 Confederate Soldiers Monument Inscription
Confederate Soldiers Monument Inscription
 Confederate Women Monument
Confederate Women Monument
Congressional Districts
Conscription
Consensual Guardianship
Consolidated White River Academy
 Constantin Gusher
Constantin Gusher
Constitutional Immunity
aka: State Sovereign Immunity
Constitutional Union
 Construction Detail
Construction Detail
Convent Inspection Act of 1915
aka: Act 130 of 1915
aka: Posey Act
Convict Lease System
 Convict Lease System Article
Convict Lease System Article
 Conway Confederate Monument
Conway Confederate Monument
 Conway Confederate Monument
Conway Confederate Monument




