Entry Category: Military Science
First Arkansas Light Artillery (CS)
 First Arkansas Light Artillery Battery
First Arkansas Light Artillery Battery
First Arkansas Light Artillery Battery (US)
First Arkansas Light Battery (African Descent) (US)
aka: Battery H, Second U.S. Colored Artillery (Light)
First Arkansas Union Cavalry (US)
First Arkansas Volunteer Infantry Regiment (African Descent) (US)
aka: Forty-sixth Regiment U.S. Colored Troops
First Arkansas Volunteer Infantry Regiment (CS)
 First Iowa Cavalry
First Iowa Cavalry
 First Regiment Flag
First Regiment Flag
Fitzhugh’s Woods, Action at
Flanagin, Harris
 Flooded Highway
Flooded Highway
 Flooding in Cotton Plant
Flooding in Cotton Plant
Floyd, John Buchanan
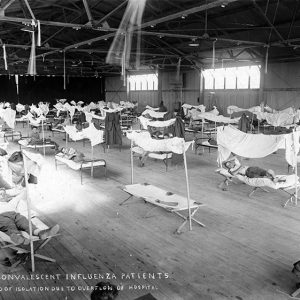 Flu Patients
Flu Patients
 Samuel Fordyce
Samuel Fordyce
Forsyth, Missouri, to Batesville, Scout from
Fort Bussey
Fort Chaffee
aka: Camp Chaffee
 Fort Chaffee Drawing
Fort Chaffee Drawing
 Fort Chaffee Drawing
Fort Chaffee Drawing
 Fort Chaffee English Lessons
Fort Chaffee English Lessons
 Fort Chaffee Newspaper
Fort Chaffee Newspaper
 Fort Chaffee Sign
Fort Chaffee Sign
 Fort Chaffee, Aerial View
Fort Chaffee, Aerial View
Fort Curtis
Fort Hindman
 Fort Hindman Attack
Fort Hindman Attack
Fort Lincoln
aka: DeValls Bluff Fortifications
 Fort Logan H. Roots Company B
Fort Logan H. Roots Company B
Fort Logan H. Roots Military Post Historic District
aka: Fort Roots
 Fort Roots Building 11; 2010
Fort Roots Building 11; 2010
 Fort Roots Building 1; 2010
Fort Roots Building 1; 2010
 Fort Roots Building 37; 1908
Fort Roots Building 37; 1908
 Fort Roots Building 37; 2010
Fort Roots Building 37; 2010
 Fort Roots Building 1; 1900
Fort Roots Building 1; 1900
 Fort Roots Building 11; 1905
Fort Roots Building 11; 1905
 Fort Logan H. Roots Officers' Quarters
Fort Logan H. Roots Officers' Quarters
 Fort Logan H. Roots Panorama
Fort Logan H. Roots Panorama
 Fort Pillow, First Position
Fort Pillow, First Position
 Fort Pillow, Third Position
Fort Pillow, Third Position
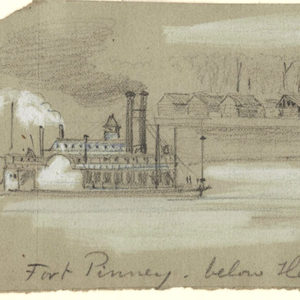 Fort Pinney
Fort Pinney




