 Irma Brown
Irma Brown
Entry Category: Government and Politics
 Irma Brown
Irma Brown
 Irma Hunter Brown
Irma Hunter Brown
Brown, Irma Lee Hunter
Brownlee, Christine Jackson
 Stephen Brundidge
Stephen Brundidge
Brundidge, Stephen, Jr.
Bryan, Leon L. “Doc”
 Bryant and Glover
Bryant and Glover
 Bryant and Nelson
Bryant and Nelson
 Bryant Brochure
Bryant Brochure
Bryant, John Winston
Bryant, Kelly
 Winston Bryant
Winston Bryant
 Bumpers in Parade
Bumpers in Parade
 Bumpers Vaccine Research Center
Bumpers Vaccine Research Center
Bumpers, Betty
 Betty Bumpers and Lily Peter
Betty Bumpers and Lily Peter
 Dale Bumpers
Dale Bumpers
Bumpers, Dale Leon
 Bumpers in Cabot
Bumpers in Cabot
Bunch, Bradley
 A. E. Bush
A. E. Bush
Bush, John
 Charles Bussey
Charles Bussey
Bussey, Charles E., Jr.
Butler, Ben F.
Butler, Turner
 Turner Butler
Turner Butler
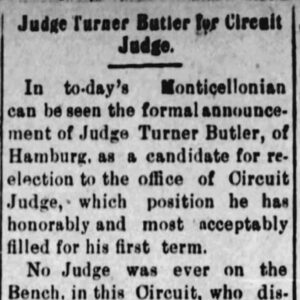 Turner Butler Candidacy Story
Turner Butler Candidacy Story
 Festus O. Butt
Festus O. Butt
Butt, Festus Orestes
Bynum, Preston Conrad
Cabe, Gloria Buford
Caldwell, Arthur Brann
Caldwell, Creed Sr.
 Calhoun County Courthouse
Calhoun County Courthouse
California Gold Rush, Effect of the
Callery, Ida Hayman
 Calvert Mansion
Calvert Mansion
 Camp Shelby Dance
Camp Shelby Dance
Campaign Finance Laws
Campbell, John
 T. W. Campbell Article
T. W. Campbell Article
Campbell, Tom Walter
Canada, Eugene “Bud”
 Canning at Dyess
Canning at Dyess
Capital Punishment
aka: Death Penalty
 Capitol Balcony
Capitol Balcony
 Capitol Construction
Capitol Construction
 Capitol Construction
Capitol Construction




