 John Williams Lynching Article
John Williams Lynching Article
Entry Category: Civil Rights and Social Change
 John Williams Lynching Article
John Williams Lynching Article
Williams, John (Lynching of)
Williams, Leonard Lee (Killing of)
 Samuel Williams
Samuel Williams
Williams, Samuel Woodrow
Williams, Sue Cowan
 Sue Cowan Williams
Sue Cowan Williams
Wilson, Alexander (Lynching of)
 Alexander Wilson Lynching Article
Alexander Wilson Lynching Article
Wilson, Hog (Lynching of)
 Hog Wilson Lynching Article
Hog Wilson Lynching Article
Wilson, Tom (Lynching of)
 Effiegene Wingo
Effiegene Wingo
Wingo, Effiegene Locke
 WKKK Headquarters
WKKK Headquarters
Woman’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU)
aka: Arkansas Woman's Christian Temperance Union
Woman’s Chronicle
 Woman's Chronicle
Woman's Chronicle
Women
Women for Constitutional Government (WCG)
Women in the Southern Tenant Farmers’ Union
 Women of the 75th U.S. Congress
Women of the 75th U.S. Congress
Women’s Action for New Directions, Arkansas Chapter
aka: Arkansas WAND
Women’s Intentional Communities
aka: Women's Land Communities
Women’s Library
Women’s Project
Women’s Suffrage Movement
Women’s Emergency Committee to Open Our Schools (WEC)
Woodman, Joe (Lynching of)
 Joe Woodman Lynching Article
Joe Woodman Lynching Article
 Woodrow Wilson Proclamation
Woodrow Wilson Proclamation
 Woodward Lynching Editorial
Woodward Lynching Editorial
 Woolworth's
Woolworth's
Wordlaw, William
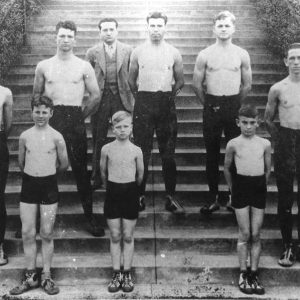 Wrestlers at School for the Deaf
Wrestlers at School for the Deaf
Wright v. Arkansas
 Wynne Lynching Article
Wynne Lynching Article
Wynne Lynching of 1892
 William Yancey Lynching Article
William Yancey Lynching Article
Yellowhammer
 Young Execution Story
Young Execution Story
Young, Charles (Lynching of)
 Rufus K. Young
Rufus K. Young




