 Buena Vista Church
Buena Vista Church
County: Ouachita
 Buena Vista Church
Buena Vista Church
 Buena Vista Church
Buena Vista Church
 Buena Vista Fire Department
Buena Vista Fire Department
Bunn, Henry Gaston
 Burkett House
Burkett House
 Camark Postcard
Camark Postcard
Camark Pottery
Camden (Ouachita County)
 Camden Log Cabin
Camden Log Cabin
 Camden Vets
Camden Vets
 Camden Aerial View
Camden Aerial View
Camden Army Air Field
aka: Harrell Field
 Camden Baptist Church
Camden Baptist Church
 Camden Barbers
Camden Barbers
 Camden Businesses
Camden Businesses
 Camden Church
Camden Church
 Camden Church
Camden Church
 Camden Church
Camden Church
 Camden Confederate Monument
Camden Confederate Monument
Camden Confederate Monument
Camden Daffodil Festival
 Camden Depot
Camden Depot
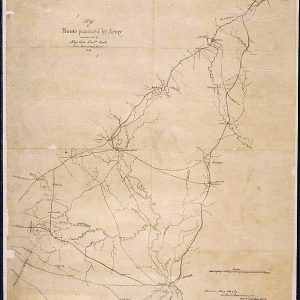 Camden Expedition Map
Camden Expedition Map
 Camden Federal Building
Camden Federal Building
 Camden Fire Department
Camden Fire Department
 Camden Gusher
Camden Gusher
 Camden Masonic Lodge
Camden Masonic Lodge
 Camden Municipal Building
Camden Municipal Building
 Camden News Building
Camden News Building
 Camden Parade
Camden Parade
 Camden River Access
Camden River Access
 Camden Scene
Camden Scene
 Camden Street Fair
Camden Street Fair
 Camden Street Scene
Camden Street Scene
 Camden Street Scene
Camden Street Scene
 Camden Street Scene
Camden Street Scene
 Camden Street Scene
Camden Street Scene
 Camden View
Camden View
Camden Water Battery
 Camden Water Battery
Camden Water Battery
 Camden Water Battery
Camden Water Battery
Camden, Skirmish at (April 15, 1864)
Captain John T. Burkett House
Carnes, Gressie Umsted
Carnes, Jack
aka: Samuel Jacob Carnes
 Entering Chidester
Entering Chidester
Chidester (Ouachita County)
 Chidester Church
Chidester Church
 Chidester Church
Chidester Church
 Chidester Fire Department
Chidester Fire Department




