 Hope Utilities
Hope Utilities
Time Period: Early Twentieth Century (1901 - 1940) - Starting with H
 Hope Utilities
Hope Utilities
 Hope Watermelon Festival
Hope Watermelon Festival
 Harry L. Hopkins
Harry L. Hopkins
Horace Estes House
 Horace Mann Gymnasium
Horace Mann Gymnasium
 Horace Mann Home Ec Building
Horace Mann Home Ec Building
Horace Mann School Historic District
 Horatio Post Office
Horatio Post Office
 Horatio Peach Harvesters
Horatio Peach Harvesters
 Elijah Whitt Horner
Elijah Whitt Horner
 Horner and Choctaw Telephone Squad
Horner and Choctaw Telephone Squad
 Hornibrook House Detail
Hornibrook House Detail
 Hornibrook House
Hornibrook House
 Horse Sale
Horse Sale
 Frank Horsfall
Frank Horsfall
 Horticulture Exhibit
Horticulture Exhibit
Horton, Zilphia Mae Johnson
Hospital Unit T
 Hospital Unit T Article
Hospital Unit T Article
 Hospital Unit T Paean
Hospital Unit T Paean
Hot Spring County Courthouse
 Hot Springs Conductors
Hot Springs Conductors
 Hot Springs Buildings
Hot Springs Buildings
Hot Springs Central Avenue Historic District
Hot Springs Confederate Monument
Hot Springs Fire of 1905
 Hot Springs Fire of 1905
Hot Springs Fire of 1905
 Hot Springs Fire of 1905
Hot Springs Fire of 1905
 Hot Springs Fire of 1905
Hot Springs Fire of 1905
 Hot Springs Fire of 1905
Hot Springs Fire of 1905
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913
Hot Springs Fire of 1913
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Central Ave.
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Central Ave.
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913
Hot Springs Fire of 1913
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Central Ave.
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Central Ave.
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Ouachita Ave.
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Ouachita Ave.
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Where It Started
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Where It Started
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913
Hot Springs Fire of 1913
Hot Springs Fire of 1913
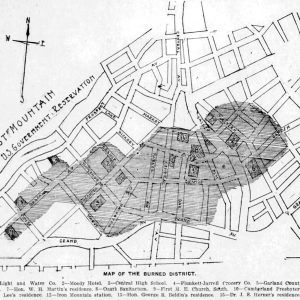 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Map
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Map
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Malvern Ave.
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Malvern Ave.
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913
Hot Springs Fire of 1913
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913
Hot Springs Fire of 1913
 Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Central Ave.
Hot Springs Fire of 1913, Central Ave.
 Hot Springs IOOF Lodge
Hot Springs IOOF Lodge
 Hot Springs Medical Journal
Hot Springs Medical Journal
Hot Springs National Guard Armory
Hot Springs Normal and Industrial Institute
aka: Mebane Academy
 Hot Springs Street Scene
Hot Springs Street Scene
 Hot Springs Trolley
Hot Springs Trolley
 Hotchkiss House
Hotchkiss House




