 Jones Speech
Jones Speech
Time Period: Early Twentieth Century (1901 - 1940)
 Jones Speech
Jones Speech
 Daniel Jones House
Daniel Jones House
 Fred Thomas Jones
Fred Thomas Jones
 Fred Jones and Nurses
Fred Jones and Nurses
Jones, Fred Thomas
Jones, Harvey
 Judge Jones Lynching Article
Judge Jones Lynching Article
Jones, Judge (Lynching of)
 Judge Jones Lynching Article
Judge Jones Lynching Article
 Judge Jones Lynching Article
Judge Jones Lynching Article
 Katie Chandler Jones
Katie Chandler Jones
Jones, Oscar Eve (O. E.)
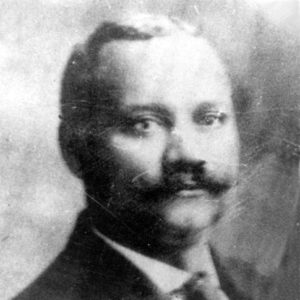 Scipio Jones
Scipio Jones
 Scipio Jones
Scipio Jones
 Scipio Jones Portrait
Scipio Jones Portrait
 Scipio A. Jones House
Scipio A. Jones House
 Scipio A. Jones House
Scipio A. Jones House
Jones, Scipio Africanus
Jones, Willa Saunders
 Willa Saunders Jones
Willa Saunders Jones
 Jones's License
Jones's License
Jonesboro Baptist College
 Jonesboro Buffaloes
Jonesboro Buffaloes
Jonesboro Church Wars
 Jonesboro Main Street
Jonesboro Main Street
 Jonesboro Soldiers
Jonesboro Soldiers
 Jonesboro Street Scene
Jonesboro Street Scene
 Jonesboro Street Scene
Jonesboro Street Scene
 Jonesboro Union Station
Jonesboro Union Station
Jonesboro, Lake City and Eastern Railroad
Joplin, Scott
 Scott Joplin
Scott Joplin
 Scott Joplin Stamp
Scott Joplin Stamp
Jordan, Lena Lowe
 Louis Jordan's Saxophone
Louis Jordan's Saxophone
Josenberger, Mame Stewart
 Mame Stewart Josenberger
Mame Stewart Josenberger
Joseph Taylor Robinson House
aka: Foster-Robinson House
 Joyzelle Campers; 1920s
Joyzelle Campers; 1920s
 Joyzelle Campers; 1930s
Joyzelle Campers; 1930s
 Orange King Judd
Orange King Judd
 Judsonia Depot
Judsonia Depot
 Judsonia Company
Judsonia Company
 Judsonia Hat Shop
Judsonia Hat Shop
 Judsonia Riverboat
Judsonia Riverboat
 Judsonia Strawberry Wagons
Judsonia Strawberry Wagons
 Judsonia Weekly Advance
Judsonia Weekly Advance
 Junction Bridge
Junction Bridge
 Junction Bridge
Junction Bridge




