 Footsie Britt
Footsie Britt
Race and Ethnicity: White - Starting with B
 Footsie Britt
Footsie Britt
 Footsie Britt
Footsie Britt
 Gay White and Footsie Britt
Gay White and Footsie Britt
 Footsie Britt Plaque
Footsie Britt Plaque
Britt, Terri Utley Amos
 Broadway Card
Broadway Card
Broadway, Joseph Eddy (Joe)
 Shane Broadway
Shane Broadway
Broadway, Shane
 Kevin Brockmeier
Kevin Brockmeier
Brockmeier, Kevin John
 Brooks and Dunn Music
Brooks and Dunn Music
 Brooks-Baxter War Cartoon
Brooks-Baxter War Cartoon
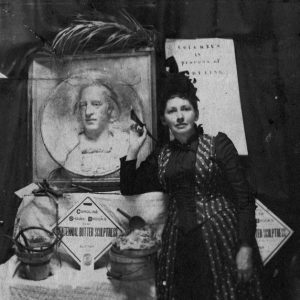 Caroline Shawk Brooks
Caroline Shawk Brooks
Brooks, Caroline Shawk
 Doyle Brooks
Doyle Brooks
 Ida Joe Brooks
Ida Joe Brooks
 Ida Joe Brooks
Ida Joe Brooks
Brooks, Ida Josephine
Brooks, John Doyle
Brooks, Joseph
 Joseph Brooks
Joseph Brooks
Brooks, William H.
 William H. Brooks
William H. Brooks
Brothers of Freedom
 Barbara Brothers
Barbara Brothers
 Charles Brough
Charles Brough
 Charles Brough
Charles Brough
 Charles Brough
Charles Brough
 Charles Brough
Charles Brough
 Charles Brough
Charles Brough
 Charles Brough
Charles Brough
Brough, Charles Hillman
Brown, Benjamin Chambers
 Benjamin Brown
Benjamin Brown
Brown, Dee
aka: Dorris Alexander Brown
 Dee Brown
Dee Brown
 Dee Brown
Dee Brown
Brown, Fountain
 Helen Gurley Brown
Helen Gurley Brown
Brown, Helen Marie Gurley
 Isaac Newton Brown
Isaac Newton Brown
Brown, J. L.
aka: James Lafayette Brown
Brown, Jacob
Brown, Jim Ed
 Jim Ed Brown and Daughter
Jim Ed Brown and Daughter
 Jim Ed Brown
Jim Ed Brown
 John Elward Brown
John Elward Brown
 John Elward Brown
John Elward Brown




