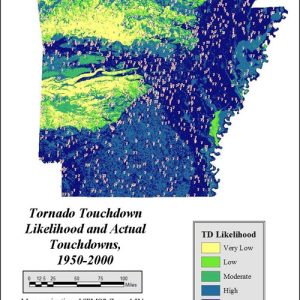
 Tornado Touchdown Map
Tornado Touchdown Map
Entry Type: Thing
 Tornado Touchdown Map
Tornado Touchdown Map
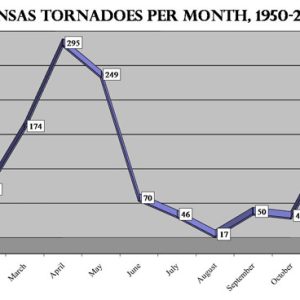 Tornado Graph
Tornado Graph
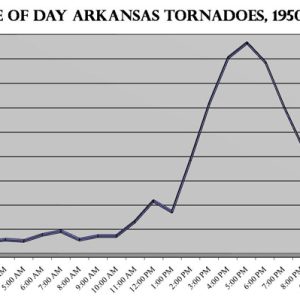 Tornado Time of Day Graph
Tornado Time of Day Graph
Tornadoes
Tower Building
 The Town that Dreaded Sundown
The Town that Dreaded Sundown
Town That Dreaded Sundown, The
Trail of Tears
Trail of Tears National Historic Trail
 Trail of Tears Marker
Trail of Tears Marker
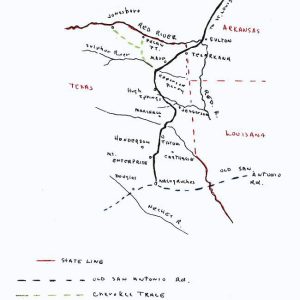 Trammel's Trace Map
Trammel's Trace Map
 Trapnall Hall
Trapnall Hall
Trees
Trematodes
aka: Flatworms
aka: Flukes
 Trichia varia
Trichia varia
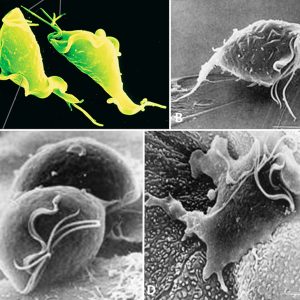 Trichomonas
Trichomonas
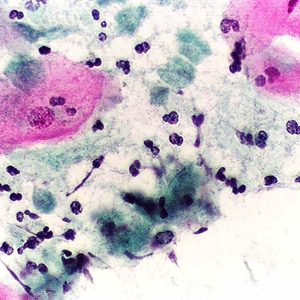 Trichomonas
Trichomonas
Trinity Episcopal Cathedral
Trinity Hospital
 Trinity Hospital Entrance
Trinity Hospital Entrance
Tripoli Mining
 Trolley
Trolley
 Troop Train
Troop Train
Tropical Cyclones
aka: Tropical Storms and Depressions
 Trout Island
Trout Island
Trucking Industry
True Grit
 True Grit by Charles Portis
True Grit by Charles Portis
 True Grit
True Grit
True Grit Trail
 Truman Visit, 1949
Truman Visit, 1949
Tuberculosis
 Tubs (Hot Springs) by Thomas Harding
Tubs (Hot Springs) by Thomas Harding
 Tucker Telephone
Tucker Telephone
 Tucker Telephone
Tucker Telephone
Tucker Telephone
Tucker Unit
aka: Tucker Prison Farm
 Tucker Unit Commissary Token
Tucker Unit Commissary Token
 Tuckerman Water Tower
Tuckerman Water Tower
Tuckerman Water Tower
 Tug and Barges on the Arkansas River
Tug and Barges on the Arkansas River
 Tulip Sign
Tulip Sign
 Tull Bridge
Tull Bridge
 Tumbling Shoals Suspension Bridge
Tumbling Shoals Suspension Bridge
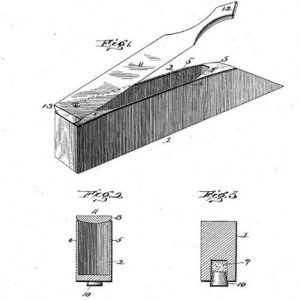 Turkey Caller
Turkey Caller
 Turkey Vulture
Turkey Vulture
 Turney Truck Fleet
Turney Truck Fleet
Turney Wood Products, Inc.
Turpentine Creek Wildlife Refuge
 Turquoise Reeds and Ozark Fiori
Turquoise Reeds and Ozark Fiori




