 SS La Salle
SS La Salle
Entry Type: Thing
 SS La Salle
SS La Salle
 SS Masan
SS Masan
 SS Ouachita Victory
SS Ouachita Victory
SS Ouachita Victory
St. Agnes Catholic Church
St. Andrew’s College
 St. Anthony's Hospital
St. Anthony's Hospital
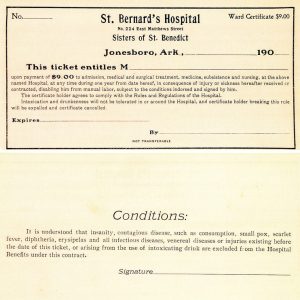 St. Bernards Medical Center Ticket
St. Bernards Medical Center Ticket
 St. Charles Ferry
St. Charles Ferry
 St. Charles Ferry
St. Charles Ferry
 St. Charles Battle Monument
St. Charles Battle Monument
St. Charles Battle Monument
 St. Charles Ferry
St. Charles Ferry
St. Edward Catholic Church
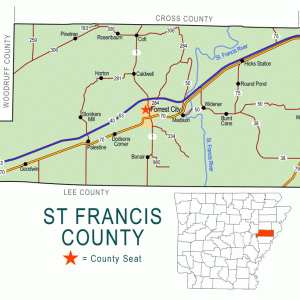 St. Francis County Map
St. Francis County Map
 St. Francis River Bridge
St. Francis River Bridge
St. Francis River
 St. Francis River Bridge
St. Francis River Bridge
 Skirmish at Tomahawk
Skirmish at Tomahawk
St. John’s Episcopal Church (Camden)
St. John’s Seminary
St. Johns’ College
St. Joseph [Steamboat]
 St. Joseph Colony Article
St. Joseph Colony Article
St. Louis Southwestern Railway
aka: Cotton Belt
St. Louis–San Francisco Railway
aka: Frisco
St. Nicholas [Steamboat]
St. Vincent Hot Springs
aka: St. Joseph's Mercy Health Center
aka: Mercy Hot Springs
aka: CHI St. Vincent Hot Springs
 St. Vincent Infirmary Dedication
St. Vincent Infirmary Dedication
 Stanly Mounds
Stanly Mounds
 Star City Commercial Historic District
Star City Commercial Historic District
 Star City Confederate Memorial
Star City Confederate Memorial
Star City Confederate Memorial
Star of India
 State Flag Garden
State Flag Garden
 State Flag Plaque
State Flag Plaque
 State History Atlas
State History Atlas
 State National Bank Building Ad
State National Bank Building Ad
State of Arkansas v. Artoria Smith
aka: Arkansas v. Smith (2015)
State of Arkansaw, The
State Parks Division
aka: State Parks
aka: Arkansas State Parks
 State Seal
State Seal
State Treasurer, Office of
aka: Office of Treasurer
Stave Mills
Stay More [Book Series]
 Steamboats
Steamboats
Steamboats
Steamboats (Civil War)
 Steamboats Illustration
Steamboats Illustration
 Stearman Crop Duster
Stearman Crop Duster




