 Eudora Ox Team
Eudora Ox Team
Entry Category: Transportation
 Eudora Ox Team
Eudora Ox Team
 F. W. Tucker Steamboat
F. W. Tucker Steamboat
 First Train to Paris
First Train to Paris
 Flippin Airport
Flippin Airport
 Flippin MoPac Tracks
Flippin MoPac Tracks
 Fordyce on the Cotton Belt Festival Cake Train
Fordyce on the Cotton Belt Festival Cake Train
Fordyce, Samuel Wesley
 Samuel Fordyce
Samuel Fordyce
Forest Rose [Steamboat]
 Fort Smith Trolley
Fort Smith Trolley
Fort Smith Regional Airport
Fort Smith to Jackson Road
 Fort Smith to Jackson Road
Fort Smith to Jackson Road
 Fort Smith Trolleys
Fort Smith Trolleys
 Foster Memorial
Foster Memorial
 Foster Memorial Highway
Foster Memorial Highway
 Fourche La Fave Bridge
Fourche La Fave Bridge
 Fourche La Fave Bridge
Fourche La Fave Bridge
 Frank R. Hill Steamboat
Frank R. Hill Steamboat
 Free Bridge
Free Bridge
 Free Bridge
Free Bridge
 Free Bridge Flyer
Free Bridge Flyer
Freedom Rides
 Freedom Rides
Freedom Rides
 Freedom Rides
Freedom Rides
 Freedom Riders Plaque
Freedom Riders Plaque
 Fulton Bridge
Fulton Bridge
 Fulton Bridge
Fulton Bridge
G. A. Thompson [Steamboat]
 G. A. Thomson Steamboat Article
G. A. Thomson Steamboat Article
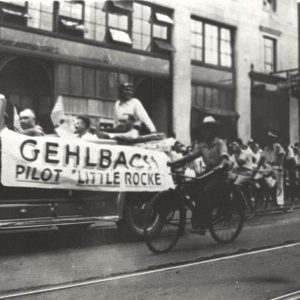 Gehlbach Parade
Gehlbach Parade
General Bem [Steamboat]
 Gentry Depot
Gentry Depot
 Gilbert Train Depot
Gilbert Train Depot
 Grading Work
Grading Work
 Grady Depot
Grady Depot
 Great River Road Sign
Great River Road Sign
Great River Road-Arkansas National Scenic Byway
Green, Marlon DeWitt
 Marlon Green
Marlon Green
 Greenwood Depot
Greenwood Depot
 Greers Ferry Reservoir Dedication Invitation
Greers Ferry Reservoir Dedication Invitation
Greers Ferry Dam and Lake
 Mike Beebe at Greers Ferry
Mike Beebe at Greers Ferry
 Bill Clinton at Greers Ferry
Bill Clinton at Greers Ferry
 Greers Ferry Dam 50th Anniversary Brochure
Greers Ferry Dam 50th Anniversary Brochure
Gulnare and Westwood, Collision of
 Gum Springs Depot
Gum Springs Depot
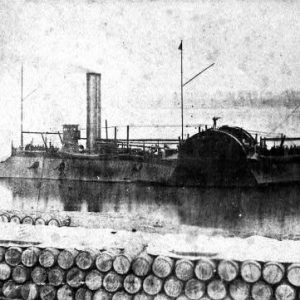 Gunboat Eastport
Gunboat Eastport
 Hackett Depot
Hackett Depot




