Entry Category: Transportation
 Pennsylvania Steamboat Article
Pennsylvania Steamboat Article
 Pennsylvania Steamboat Article
Pennsylvania Steamboat Article
 Pennywit Obituary
Pennywit Obituary
Pennywit, Philip
Persian [Steamboat]
 Persian Steamboat Article
Persian Steamboat Article
 Persian Steamboat Article
Persian Steamboat Article
 Petit Jean River at Danville
Petit Jean River at Danville
Philip Pennywit [Steamboat]
Pig Trail Scenic Byway
 Pine Bluff Hotel
Pine Bluff Hotel
Plane Crash of January 14, 1936
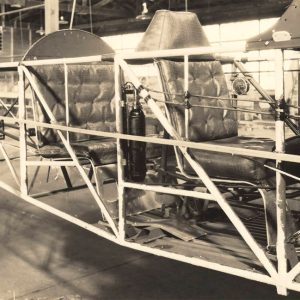 Plane Interior
Plane Interior
 Pocahontas Bridge
Pocahontas Bridge
Pocahontas [Steamboat]
 Pocahontas Depot
Pocahontas Depot
 Pocahontas Steamboat Article
Pocahontas Steamboat Article
 Portia Depot
Portia Depot
 Portland Depot
Portland Depot
 Potts Family Marker
Potts Family Marker
 Potts Inn
Potts Inn
 Poyen Depot
Poyen Depot
 Prague Depot
Prague Depot
 Prescott Depot
Prescott Depot
 Prescott Railroad Mural
Prescott Railroad Mural
 Pyatt Depot
Pyatt Depot
 Railroad Development
Railroad Development
 Railroad Tank
Railroad Tank
 Railroad Ticket Office
Railroad Ticket Office
 Railroad Workers
Railroad Workers
 Railroad Workers near Jonesboro
Railroad Workers near Jonesboro
Railroads
 Railway at Penters Bluff
Railway at Penters Bluff
 Railway Workers
Railway Workers
 Red River Bridge
Red River Bridge
 Red River Bridge
Red River Bridge
 Red River Raft
Red River Raft
 Redfield Depot
Redfield Depot
 Redfield Viaduct
Redfield Viaduct
Remmel Dam
aka: Lake Catherine
 Rice Seed Loading
Rice Seed Loading
 Rich Mountain School Bus
Rich Mountain School Bus
 Rio Vista Depot
Rio Vista Depot
 Rison Depot
Rison Depot
Roads and Highways
Rob Roy [Steamboat]
 Rob Roy Steamboat Article
Rob Roy Steamboat Article
 Rock ‘n’ Roll Highway Route Sign
Rock ‘n’ Roll Highway Route Sign
 Rock Island Bridge
Rock Island Bridge




