 Arkansas Academy of Science Story
Arkansas Academy of Science Story
Entry Category: Science and Medicine
 Arkansas Academy of Science Story
Arkansas Academy of Science Story
 Arkansas Ambloplites
Arkansas Ambloplites
Arkansas Association of Black Psychology Professionals
 Arkansas Baitfish and the Silver Carp
Arkansas Baitfish and the Silver Carp
 Arkansas Baptist Hospital
Arkansas Baptist Hospital
 Arkansas Baptist Medical Center
Arkansas Baptist Medical Center
 Arkansas Basses
Arkansas Basses
Arkansas Biosciences Institute (ABI)
Arkansas Black Apple
 Arkansas Black Apple Ad
Arkansas Black Apple Ad
Arkansas Blood Labeling Bill
aka: HB 385
 Arkansas Blue Cross and Blue Shield
Arkansas Blue Cross and Blue Shield
Arkansas Children’s Colony
aka: Conway Human Development Center
Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH)
 Arkansas College of Medicine
Arkansas College of Medicine
 Arkansas Conference College
Arkansas Conference College
 Arkansas Country Doctor Museum
Arkansas Country Doctor Museum
Arkansas Country Doctor Museum (ACDM)
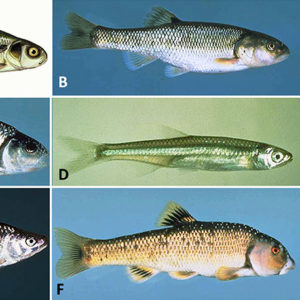 Arkansas Cyprinids
Arkansas Cyprinids
Arkansas Darter
aka: Etheostoma cragini
Arkansas Department of Health (ADH)
Arkansas Division of Information Systems (DIS)
Arkansas Entomological Society
Arkansas Fatmucket
aka: Lampsilis powellii
 AGC Mineral Set
AGC Mineral Set
Arkansas Geological Survey (AGS)
Arkansas Health Center
 Arkansas Health Center
Arkansas Health Center
 Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge
Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge
 Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge
Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge
 Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge
Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge
 Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge View
Arkansas Highway 57 Bridge View
 Arkansas Insane Asylum
Arkansas Insane Asylum
Arkansas Medical Society
Arkansas Medical, Dental, and Pharmaceutical Association
Arkansas Methodist Medical Center
Arkansas Mycological Society
Arkansas Native Plant Society
Arkansas Nurses Association
 Arkansas Post Dedication
Arkansas Post Dedication
Arkansas Research Alliance
Arkansas Research and Test Station
Arkansas Science and Technology Authority (ASTA)
Arkansas Sky Observatories
Arkansas State Crime Laboratory
Arkansas State Horticultural Society (ASHS)
Arkansas State Hospital
 Arkansas State Hospital
Arkansas State Hospital
 Arkansas State Hospital
Arkansas State Hospital
 Arkansas State Hospital
Arkansas State Hospital




