 Granville Warden Murder Story
Granville Warden Murder Story
Entry Category: Law
 Granville Warden Murder Story
Granville Warden Murder Story
Graves, Levi (Lynching of)
 Levi Graves Lynching Article
Levi Graves Lynching Article
Green (Lynching of)
 Green Lynching Article
Green Lynching Article
Green, Crane (Lynching of)
 Crane Green Lynching Article
Crane Green Lynching Article
Green, Steve
Greenhaw, Karl
 Greenwood Jail
Greenwood Jail
 Bob Greenwood Lynching Article
Bob Greenwood Lynching Article
Greenwood, Bob (Lynching of)
Greeson, Martin White
Gregg, Lafayette
 Lafayette Gregg
Lafayette Gregg
Gridiron
Gross, Tabbs
 Tabbs Gross Article
Tabbs Gross Article
Guerilla Execution of 1864 (Little Rock)
 James H. Gunter
James H. Gunter
Gunter, James Houston (Jim), Jr.
 Gurdon Jail
Gurdon Jail
 Gurdon Jail
Gurdon Jail
Guy v. Daniel
aka: Abby Guy v. William Daniel
 Nat Hadley Lynching Article
Nat Hadley Lynching Article
Haley, Loy (Lynching of)
 Hall and Edmunds Execution Story
Hall and Edmunds Execution Story
Hall, Frank (Execution of)
Hallum, John
 John Hallum Death
John Hallum Death
Hamilton and Ludberry (Lynching of)
Hamilton, Henry (Reported Lynching of)
 Henry Hamilton Lynching Article
Henry Hamilton Lynching Article
 Hammond Packing Company Story
Hammond Packing Company Story
 Hammond Packing Company Story
Hammond Packing Company Story
Hammond Packing Company v. Arkansas
 Hampton Lynching Article
Hampton Lynching Article
Hampton Race War of 1892
aka: Calhoun County Race War of 1892
 James R. Hannah
James R. Hannah
Hannah, James Robert (Jim)
 Hardin Commutation Story
Hardin Commutation Story
 Hardin Murder Story
Hardin Murder Story
 W. H. Hardin Lynching Story
W. H. Hardin Lynching Story
 W. H. Hardin Lynching Story
W. H. Hardin Lynching Story
Hardin, Will H. (Lynching of)
Harper, Charles Augustus (C. A.)
Harper, John (Execution of)
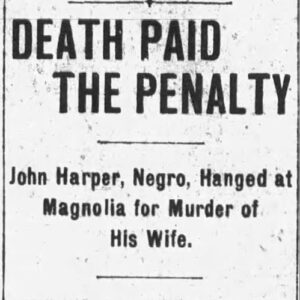 John Harper Execution Story
John Harper Execution Story
 William Harper Execution Story
William Harper Execution Story
 Harris Lynching
Harris Lynching




