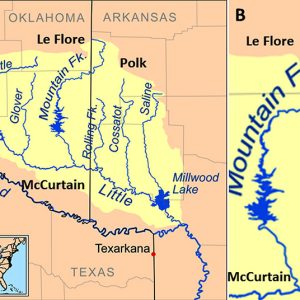
 Mountain Fork River Map
Mountain Fork River Map
Entry Category: Land and Resources
 Mountain Fork River Map
Mountain Fork River Map
 Mountain Home Cotton
Mountain Home Cotton
 Mountain Valley Spring
Mountain Valley Spring
Mulberry River
 Murfreesboro Cotton Warehouse
Murfreesboro Cotton Warehouse
Muscadine
aka: Vitus rotundifolia
Museum of the Arkansas Grand Prairie
 Museum of the Arkansas Grand Prairie
Museum of the Arkansas Grand Prairie
 Nacatoch Ravines Natural Area
Nacatoch Ravines Natural Area
National Fish Hatcheries
 Natural Bridge
Natural Bridge
 Natural Bridge
Natural Bridge
 Natural Bridge
Natural Bridge
 Natural Bridge Cabin
Natural Bridge Cabin
 Natural Bridge Display
Natural Bridge Display
 Natural Bridge Display
Natural Bridge Display
 Natural Bridge Display
Natural Bridge Display
 Natural Bridge Display
Natural Bridge Display
Natural Steps (Pulaski County)
Nature Conservancy of Arkansas
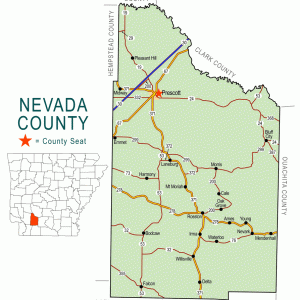 Nevada County Map
Nevada County Map
New Madrid Earthquakes of 1811-1812
New Madrid Fault
aka: New Madrid Seismic Zone
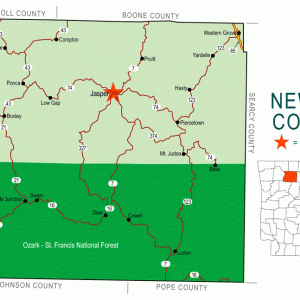 Newton County Map
Newton County Map
 Night Riders Article
Night Riders Article
Nimrod Dam and Lake
Nix, Joe Franklin
 Norfork Dam
Norfork Dam
 Norfork Dam Construction
Norfork Dam Construction
 Norphlet Fire
Norphlet Fire
North Fork River
 North Fork River Bridge
North Fork River Bridge
 North Little Rock Flood
North Little Rock Flood
 North Little Rock Flood
North Little Rock Flood
 North Little Rock Flood
North Little Rock Flood
 North Little Rock Flood
North Little Rock Flood
 North Wilson Vanadium Mine
North Wilson Vanadium Mine
Northern Snakehead
aka: Channa argus
aka: Snakehead
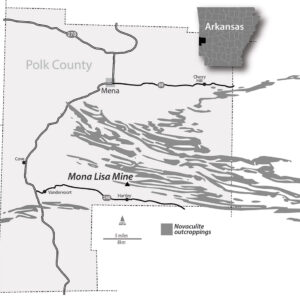 Novaculite Outcroppings
Novaculite Outcroppings
 Ouachita River at Oden
Ouachita River at Oden
Official State Grape
aka: Cynthiana Grape
 Oil Field Workers
Oil Field Workers
Oil Industry
 Oil Trough Cotton Gin
Oil Trough Cotton Gin
 Oil Trough Park
Oil Trough Park
 Oil Well Flow
Oil Well Flow
 Old Post Park
Old Post Park
OMNI Center for Peace, Justice and Ecology
 Ouachita County Map
Ouachita County Map




