 1907 Flood
1907 Flood
Entry Category: Land and Resources
 1907 Flood
1907 Flood
 1961 Flood
1961 Flood
 1961 Flood
1961 Flood
A. M. Bohnert Rice Plantation Pump No. 2 Engine
Abernathy Spring
 Abernathy Spring
Abernathy Spring
 Abernathy Spring
Abernathy Spring
 ADC Workers
ADC Workers
 Aerial Seeding
Aerial Seeding
 African American Flood Refugees
African American Flood Refugees
Agricultural Adjustment Act
Agricultural Wheel
 Agricultural Wheel Constitution
Agricultural Wheel Constitution
Agriculture
 Alcoa Aluminum
Alcoa Aluminum
Alexander, Harold Edward
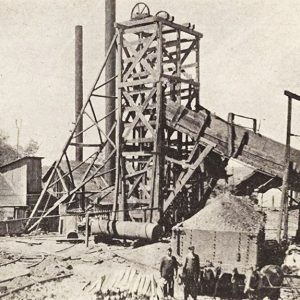 Alix Mine
Alix Mine
 Aluminum Company of America
Aluminum Company of America
American Viticultural Areas
aka: Viticultural Areas
American Wine Society – Arkansas Chapter
 Amethyst Geode
Amethyst Geode
 Amity Peach Pickers
Amity Peach Pickers
 Anderson Farms Tank
Anderson Farms Tank
 Anthony Oak Flooring Plant in Magnolia
Anthony Oak Flooring Plant in Magnolia
 Anthony Timberlands, Inc.
Anthony Timberlands, Inc.
Anthony Timberlands, Inc.
 Anthracite Mining
Anthracite Mining
 Antimony City Article
Antimony City Article
Antimony Mining
 Antimony Mining Article
Antimony Mining Article
Antoine River
 Apple Display
Apple Display
 Apple Festival Float
Apple Festival Float
Apple Industry
Aquaculture
 Arkadelphia Lumber Company
Arkadelphia Lumber Company
Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station (AAES)
Arkansas Black Apple
Arkansas Chapter of the Sierra Club
aka: Sierra Club
 Arkansas City Cotton Picker
Arkansas City Cotton Picker
 Arkansas City Flood
Arkansas City Flood
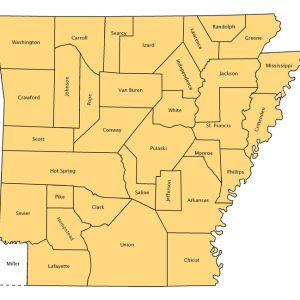 Arkansas Counties Map, 1836
Arkansas Counties Map, 1836
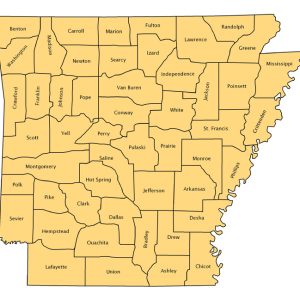 Arkansas Counties Map, 1850
Arkansas Counties Map, 1850
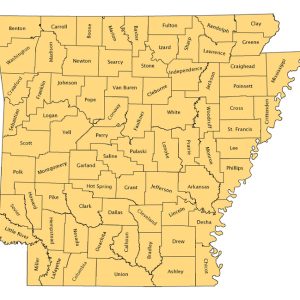 Arkansas Counties Map, 2005
Arkansas Counties Map, 2005
 Arkansas County Map
Arkansas County Map




