 Segregationist Rally
Segregationist Rally
Entry Category: Educational Issues and Controversies
 Segregationist Rally
Segregationist Rally
Sex Education
 Shooting Tribute
Shooting Tribute
Six Pioneers
 Six Pioneers Sign
Six Pioneers Sign
 STOP Rally
STOP Rally
Stop This Outrageous Purge (STOP)
 STOP Ads
STOP Ads
 STOP Ad
STOP Ad
 STOP Ad
STOP Ad
 Students and Soldiers
Students and Soldiers
 Adolphine Fletcher Terry
Adolphine Fletcher Terry
 Adolphine and David Terry
Adolphine and David Terry
 Adolphine Fletcher Terry
Adolphine Fletcher Terry
 Adolphine Fletcher Terry
Adolphine Fletcher Terry
 Mary Fletcher Terry
Mary Fletcher Terry
 Mary Fletcher Terry
Mary Fletcher Terry
Thomas, Jefferson Allison
 Three of the North Little Rock Six
Three of the North Little Rock Six
 Thurgood Marshall and Central High Students
Thurgood Marshall and Central High Students
 Ethel Tompkins
Ethel Tompkins
Trickey, Minnijean Brown
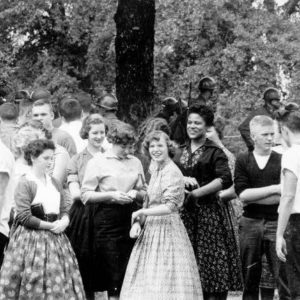 Minnijean Brown with Classmates
Minnijean Brown with Classmates
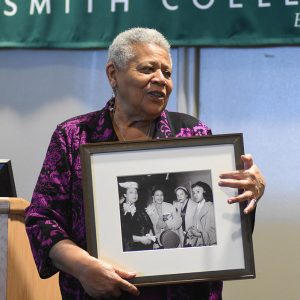 Minnijean Brown Trickey
Minnijean Brown Trickey
Van Buren Schools, Desegregation of
 Van Buren Desegregation
Van Buren Desegregation
Wair, Thelma Jean Mothershed
 WEC Meeting
WEC Meeting
Westside School Shooting
 Westside Memorial
Westside Memorial
 Westside Middle School
Westside Middle School
 White Protesters
White Protesters
 White Protesters
White Protesters
 WEC Members Brewer, Terry, and House
WEC Members Brewer, Terry, and House




