 WCTU Flag
WCTU Flag
Time Period: Early Twentieth Century (1901 - 1940) - Starting with W
 WCTU Flag
WCTU Flag
Woman’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU)
aka: Arkansas Woman's Christian Temperance Union
 Woman's City Club
Woman's City Club
 Woman's Committee
Woman's Committee
Woman’s Progressive Club (Wynne)
 Womble Businesses
Womble Businesses
Womble District Administration House Number 1
 Womble, 1914
Womble, 1914
Women in the Southern Tenant Farmers’ Union
 Women of the 75th U.S. Congress
Women of the 75th U.S. Congress
Women of the Ku Klux Klan (WKKK)
 Women's Community Band Shell
Women's Community Band Shell
Women’s Community Club Band Shell
 Women's Suffrage Rally
Women's Suffrage Rally
 Women's Suffrage Rally
Women's Suffrage Rally
 Wonder State Resolution
Wonder State Resolution
Wonderland Cave
 Wonderland Cave
Wonderland Cave
 Wonderland Cave Band
Wonderland Cave Band
 C. D. Wood Editorial
C. D. Wood Editorial
Wood, Carroll D.
 Carroll D. Wood
Carroll D. Wood
 Carroll D. Wood Supporters Article
Carroll D. Wood Supporters Article
 Woodland College Article
Woodland College Article
Woodman, Joe (Lynching of)
 Joe Woodman Lynching Article
Joe Woodman Lynching Article
 Woodrow Wilson Proclamation
Woodrow Wilson Proclamation
Woodruff County Courthouse
 Woodruff County News
Woodruff County News
 Woodruff School
Woodruff School
 Woods Colt, The
Woods Colt, The
Woods Colt, The
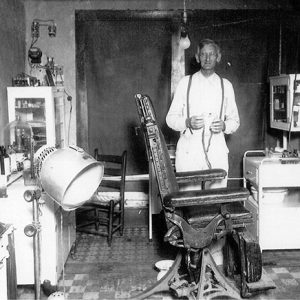 Dr. O. S. Woods
Dr. O. S. Woods
Woodward, William (Lynching of)
Wool Hat Boys
Wordlaw, William
 Worker Village
Worker Village
Works Progress Administration (WPA)
World War I
aka: The Great War
World War I Markers and Memorials
 World War I Soldiers
World War I Soldiers
 World War I Soldiers
World War I Soldiers
Worms [Medical Condition], Traditional Remedies
aka: Intestinal Parasites
 W. B. Worthen
W. B. Worthen
WPA Slave Narratives
aka: Slave Narratives
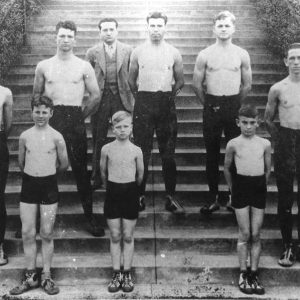 Wrestlers at School for the Deaf
Wrestlers at School for the Deaf
 Richard N. Wright
Richard N. Wright
Wright, Richard Nathaniel
 WWII Soldiers and Sailors
WWII Soldiers and Sailors
 Dr. Will Wyatt's Office
Dr. Will Wyatt's Office




