 Baptist Academy Article
Baptist Academy Article
Time Period: Early Twentieth Century (1901 - 1940) - Starting with B
 Baptist Academy Article
Baptist Academy Article
 Baptist Convention
Baptist Convention
Barham, Ella (Murder of)
 Barham Family
Barham Family
 Barham Sisters
Barham Sisters
 Baring Cross Bridge; 1927
Baring Cross Bridge; 1927
 Baring Cross Bridge
Baring Cross Bridge
 Baring Cross Bridge
Baring Cross Bridge
 Barker Home
Barker Home
Barker-Karpis Gang
aka: Ma Barker Gang
 Fred Barker
Fred Barker
 Ma Barker
Ma Barker
 Arthur "Doc" Barker
Arthur "Doc" Barker
 Catherine Barker
Catherine Barker
Barker, Catherine Sweazey
 Barlow Hotel
Barlow Hotel
 Barlow Hotel Porch
Barlow Hotel Porch
 Barlow Hotel Postcard
Barlow Hotel Postcard
Barnett, John (Lynching of)
 John Barnett Lynching Article
John Barnett Lynching Article
 Barnett's Store
Barnett's Store
 John Barnhill
John Barnhill
 Barrow and Jones
Barrow and Jones
 Barrow, Clyde
Barrow, Clyde
Bart Tully [Steamboat]
 Bart Tully Article
Bart Tully Article
 Bart Tully Article
Bart Tully Article
Bartell, Fred Wallace
 Bartell House
Bartell House
 Fred Bartell
Fred Bartell
Bartlett, E. M.
aka: Eugene Monroe Bartlett Sr.
Barton, Dorothy Yarnell
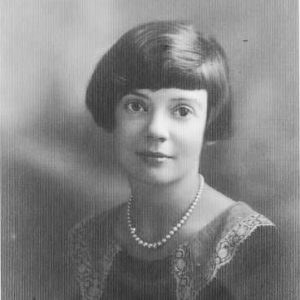 Dorothy Yarnell Barton
Dorothy Yarnell Barton
 T. H. Barton
T. H. Barton
 T. H. Barton
T. H. Barton
Barton, Thomas Harry
 Basin Park Hotel
Basin Park Hotel
 Batesville Pioneers
Batesville Pioneers
 Raymond H. Bass
Raymond H. Bass
 Sim Bateman
Sim Bateman
Bates School House
 L. C. and Daisy Bates Museum
L. C. and Daisy Bates Museum
 Batesville Billiards Hall
Batesville Billiards Hall
 Batesville 1915 Flood
Batesville 1915 Flood
 Batesville Basketball
Batesville Basketball
Batesville Confederate Monument
 Batesville Grocer
Batesville Grocer
 Batesville High School
Batesville High School
Batesville National Guard Armory
aka: Abraham Armory
 Batesville Saloon
Batesville Saloon




