Time Period: Post-Reconstruction through the Gilded Age (1875 - 1900)
 St. Joseph Colony Article
St. Joseph Colony Article
 St. Mary's Convent
St. Mary's Convent
 St. Scholastica Monastery
St. Scholastica Monastery
St. Scholastica Monastery
 St. Vincent Infirmary
St. Vincent Infirmary
Staner, Tom (Trial and Execution of)
Stanley, Henry Morton
aka: John Rowlands
 Stanly Mounds
Stanly Mounds
 Stansberry Execution Story
Stansberry Execution Story
Stansberry, John (Execution of)
 Belle Starr
Belle Starr
Starr, Belle
aka: Myra Maybelle Shirley
 Belle Starr and Blue Duck
Belle Starr and Blue Duck
 Belle Starr
Belle Starr
 Belle Starr Arrest Warrant
Belle Starr Arrest Warrant
 Steamboats Illustration
Steamboats Illustration
Stephens, Charlotte Andrews (Lottie)
Stewart, Charles (Lynching of)
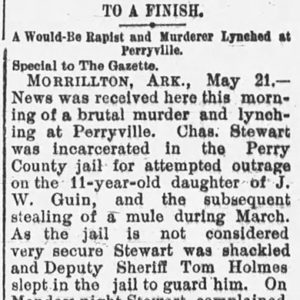 Charles Stewart Lynching Article
Charles Stewart Lynching Article
 Arthur E. Stilwell
Arthur E. Stilwell
 Stone County Lynching Article
Stone County Lynching Article
Stone County Lynching of 1898
 Strother Mill
Strother Mill
Stuart, Mary Routh McEnery
aka: Ruth McEnery Stuart
 Stuttgart Street Scene
Stuttgart Street Scene
Stuttgart Training School
aka: Stuttgart College
aka: Stuttgart Normal School
 Stuttgart Training School
Stuttgart Training School
 Subiaco Monastery
Subiaco Monastery
Sulphur Rock Male and Female Academy
Sulphur Springs Cemetery
Sunnyside Plantation
 Sunnyside Plantation Convict Labor Article
Sunnyside Plantation Convict Labor Article
 Sylvester Churchill Lynching Article
Sylvester Churchill Lynching Article
 Mary B. Talbert
Mary B. Talbert
Talbert, Mary Burnett
 Lewis Tappan
Lewis Tappan
Tate Plantation Strike of 1886
 Tate Plantation Strike of 1886
Tate Plantation Strike of 1886
Tatum, Luke (Execution of)
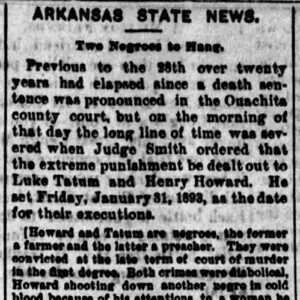
 Luke Tatum Execution Article
Luke Tatum Execution Article
 Luke Tatum Execution Article
Luke Tatum Execution Article
 Luke Tatum Execution Story
Luke Tatum Execution Story
 Luke Tatum Execution Story
Luke Tatum Execution Story
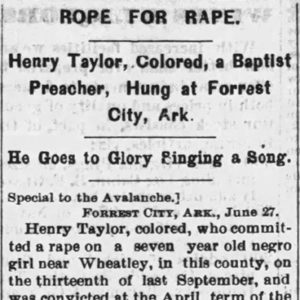 Taylor Execution Article
Taylor Execution Article
 George Edwin Taylor
George Edwin Taylor
Taylor, Henry (Execution of)
 Jack Taylor Execution Article
Jack Taylor Execution Article




