Time Period: Louisiana Purchase through Early Statehood (1803 - 1860)
aka: Old Cherokee Boundary Line
 Chicot County Lynching Article
Chicot County Lynching Article
Chicot County Lynching of 1836
aka: Bunch (Lynching of)
Choctaw Boundary Line
 Choctaw Boundary Line
Choctaw Boundary Line
Choctaw Scrip
Cholera
Circuit Riders
 William Clark
William Clark
Clarksville [Steamboat]
 Henry Clay
Henry Clay
Clendenin, John J.
Clermont No. 2 [Steamboat]
 Clermont Steamboat Article
Clermont Steamboat Article
 Clermont Steamboat Article
Clermont Steamboat Article
Collins, Richard D’Cantillon
 Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
 Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
Columbia (Chicot County)
 Columbia County Courthouse
Columbia County Courthouse
Comet [Steamboat]
 Comet Article
Comet Article
Compere, Lee
 Lee Compere and Wife
Lee Compere and Wife
 Lee Compere
Lee Compere
Congress and Saladin, Collision of
 Congress and Saladin, Collision of
Congress and Saladin, Collision of
Constitutional Union
 Conway Law Ad
Conway Law Ad
Conway-Crittenden Duel
aka: Crittenden-Conway Duel
 Conway-Crittenden Duel Story
Conway-Crittenden Duel Story
Conway, Elias Nelson
 Elias Nelson Conway
Elias Nelson Conway
Conway, Henry Wharton
 James Conway
James Conway
 James Conway
James Conway
Conway, James Sevier
Conway, Polly
aka: Mary Jane Bradley Conway
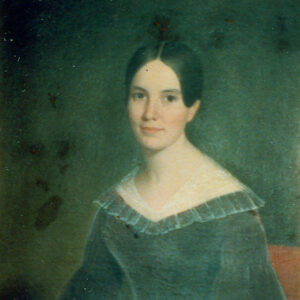 Polly Conway
Polly Conway
 Cosgrove Execution Story
Cosgrove Execution Story
 Charles Cosgrove
Charles Cosgrove
Cosgrove, Charles (Execution of)
Cote Joyeuse and Talma, Collision of
 Cote Joyeuse Steamboat Ad
Cote Joyeuse Steamboat Ad
 Cote Joyeuse Steamboat Article
Cote Joyeuse Steamboat Article
Crawford County Executions of 1843
 William Crawford
William Crawford
Crittenden County Lynching of 1840
Crittenden, Robert
 Robert Crittenden
Robert Crittenden




