Entry Category: Units and Organizations
aka: Fifth Arkansas Volunteer Infantry (African Descent)
113th United States Colored Infantry (US)
aka: Sixth Arkansas Volunteer Infantry (African Descent)
 154th Observation Squadron
154th Observation Squadron
 154th Observation Squadron
154th Observation Squadron
 154th Observation Squadron
154th Observation Squadron
 15th (NW) Arkansas Flag
15th (NW) Arkansas Flag
 17th Infantry Flag
17th Infantry Flag
 1st and 15th Infantry Regiment Flag
1st and 15th Infantry Regiment Flag
 22nd/35th Arkansas Infantry (CS) Flag
22nd/35th Arkansas Infantry (CS) Flag
312th Field Signal Battalion’s Pigeon Department
 39th Brigade Support Battalion
39th Brigade Support Battalion
 6th and 7th Infantry Regiment Flag
6th and 7th Infantry Regiment Flag
 6th Infantry Flag
6th Infantry Flag
 6th Volunteer Infantry Flag
6th Volunteer Infantry Flag
 8th and 19th Infantry Regiment Flag
8th and 19th Infantry Regiment Flag
 Alaska Defense Corps Patch
Alaska Defense Corps Patch
 Aluminum Bowl Coverage
Aluminum Bowl Coverage
Arkansas Department of Veterans Affairs (ADVA)
Arkansas Mounted Rifles [Civil War]
Arkansas Mounted Rifles [Mexican War]
Arkansas National Guard
aka: Arkansas Department of the Military
 Arkansas National Guard 153rd Insignia
Arkansas National Guard 153rd Insignia
Arkansas State Guard
Arkansas State Troops (CS)
aka: Army of Arkansas
Arkansas Wing, Civil Air Patrol
Battery E, Second U.S. Colored Artillery (Light)
Bean’s Rangers
 Bean's Rangers
Bean's Rangers
Black Union Troops
aka: African American Union Troops
aka: United States Colored Troops
 C-130 over Little Rock
C-130 over Little Rock
 CAP Aircraft
CAP Aircraft
Churchill’s Arkansas Division (CS)
 Clarksville UCV
Clarksville UCV
 Colored Regiments Recruitment Poster
Colored Regiments Recruitment Poster
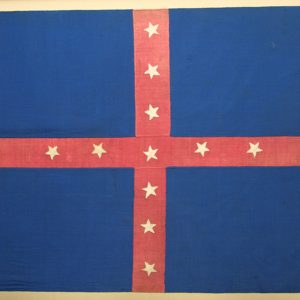 Dobbins's Cavalry Flag
Dobbins's Cavalry Flag
 Eagle Rangers
Eagle Rangers




