calsfoundation@cals.org
Entries A–Z














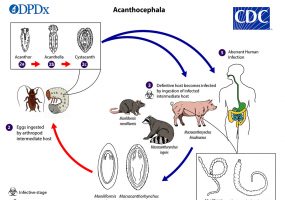
aka: Thorny-Headed Worms





aka: Anti-Whitecapping Law



aka: Arkansas's Free Negro Expulsion Act of 1859







aka: HB 1570





