Gender: Male - Starting with L
 Jack Lavey
Jack Lavey
Lavy, Thomas Lewis
 John Law
John Law
 Jay Lawhon
Jay Lawhon
 Jay Lawhon
Jay Lawhon
Lawhon, Jay Noal
 James Lawrence
James Lawrence
 Tracy Lawrence
Tracy Lawrence
Lawrence, Tracy Lee
 Tracy Lawrence
Tracy Lawrence
Lawrence, William M.
 William Lawrence
William Lawrence
Lay, Henry Champlin
Leavy, Calvin James “Slim”
 Calvin Leavy
Calvin Leavy
Lebow (Lynching of)
Ledbetter, Calvin Reville (Cal), Jr.
 Cal Ledbetter
Cal Ledbetter
Lee County Executions of 1881
Lee, Burwell
Lee, Clifton Phifer (Cliff)
Lee, Daniel Lewis (Execution of)
Lee, Haeng Ung
Lee, Hubert L.
 Hubert L. Lee
Hubert L. Lee
 Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
 Leflar and Pryor
Leflar and Pryor
 Robert A. Leflar
Robert A. Leflar
Leflar, Robert Allen
 Walter Lemke
Walter Lemke
 Walter Lemke
Walter Lemke
Lemke, Walter John
Lemley, Harry Jacob Jr.
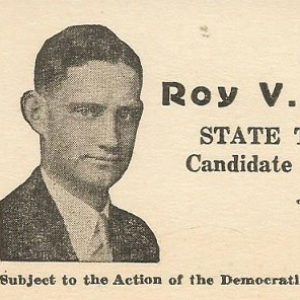 Leonard Campaign
Leonard Campaign
LeSane, Henry (Execution of)
Lester, Julius
Levels, Jacob (Execution of)
Levine, Sam M.
Lewis, Charles (Lynching of)
Lewis, David Levering
Lewis, David S. (Execution of)
 Henry J. Lewis
Henry J. Lewis
Lewis, Henry Jackson
 Henry Jackson Lewis
Henry Jackson Lewis
Lewis, Paul Tyrone
Lewis, Sanford (Lynching of)
 Sanford Lewis Lynching
Sanford Lewis Lynching




