Entry Type: Thing
 Amphipod
Amphipod
 Amphipods
Amphipods
Amphipods
aka: Scuds
Amtrak
 Anagama Fired Jar
Anagama Fired Jar
 Andrews Lure Co. Flyer
Andrews Lure Co. Flyer
Angus McLeod House
Annals of Arkansas
 Annelid Examples
Annelid Examples
Annelids
aka: Segmented Worms
 Anthony Oak Flooring Plant in Magnolia
Anthony Oak Flooring Plant in Magnolia
Anthony Timberlands, Inc.
 Anti-Amendment 59 Brochure
Anti-Amendment 59 Brochure
 Anti-Amendment 59 Campaign
Anti-Amendment 59 Campaign
 Anti-Bolshevism Act
Anti-Bolshevism Act
Anti-Catholicism
Anti-miscegenation Laws
Anti-Semitism
 Antimony City Article
Antimony City Article
Antimony Mining
 Antimony Mining Article
Antimony Mining Article
Antitrust Laws and Lawsuits (Progressive Era)
 Antivenins
Antivenins
 Antlion
Antlion
 Antlion Pit Trap
Antlion Pit Trap
 Antoine Water Tower
Antoine Water Tower
Antoine River
 AOUW Ad
AOUW Ad
 AP&L Offices
AP&L Offices
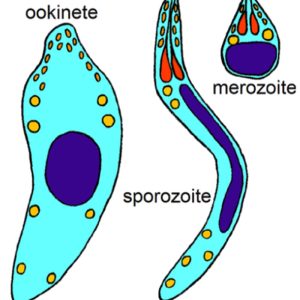 Apicomplexan Cell Types
Apicomplexan Cell Types
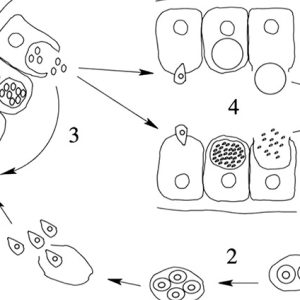 Apicomplexan Life Cycle
Apicomplexan Life Cycle
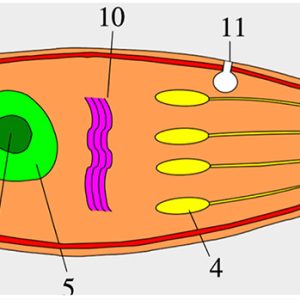 Apicomplexan Morphology
Apicomplexan Morphology
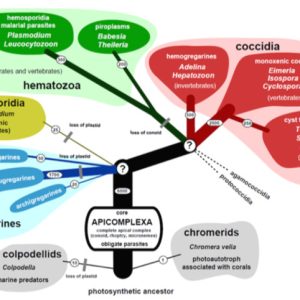 Apicomplexan Species
Apicomplexan Species
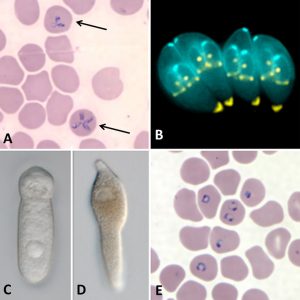 Apicomplexans
Apicomplexans
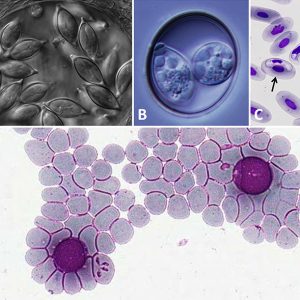 Apicomplexans Examples
Apicomplexans Examples
Apicomplexans
aka: Sporozoans
Appeal of the Arkansas Exiles to Christians throughout the World
 Apple Blossom, Official State Flower
Apple Blossom, Official State Flower
 Apple Blossom Postcard
Apple Blossom Postcard
 Apple Float
Apple Float
Apple Industry
 Applied Entomology by William Baerg
Applied Entomology by William Baerg
Aquaculture
Arachnids
 Archaeological Fakes
Archaeological Fakes
Architectural Styles
 Arcyria cinerea
Arcyria cinerea
 Arcyria denudata
Arcyria denudata




