 The Bashful Bachelor
The Bashful Bachelor
Entry Type: Thing - Starting with B
 The Bashful Bachelor
The Bashful Bachelor
Basketball
Basketry
 Daisy Bates Gravestone
Daisy Bates Gravestone
Bates School House
Batesville Confederate Monument
Batesville Daily Guard
Batesville National Guard Armory
aka: Abraham Armory
Batesville Regional Airport
 Bathhouse Row Certification Document
Bathhouse Row Certification Document
 Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans
Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans
Bats
 Battery A Marker
Battery A Marker
 Battery B Marker
Battery B Marker
 Battery C
Battery C
 Battery C Cannon
Battery C Cannon
 Battery C Marker
Battery C Marker
 Battery D Marker
Battery D Marker
 Battle of Arkansas Post Marker
Battle of Arkansas Post Marker
 Battle of Helena Monument
Battle of Helena Monument
 Battle of Lundy's Lane Soldiers' Monument
Battle of Lundy's Lane Soldiers' Monument
 "The Battle of New Orleans," Performed by Jimmy Driftwood
"The Battle of New Orleans," Performed by Jimmy Driftwood
 Battle of Reed's Bridge
Battle of Reed's Bridge
Bauxite and Northern Railroad
Bauxite Historical Association and Museum
Bauxite Mining
 Bauxite Mural
Bauxite Mural
 Bauxite, Official State Rock
Bauxite, Official State Rock
Baxter Bulletin
 Baxter Bulletin
Baxter Bulletin
Baxter County Courthouse
 Bull Shoals Dam Painting
Bull Shoals Dam Painting
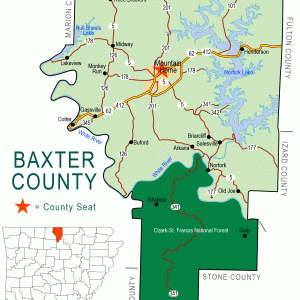 Baxter County Map
Baxter County Map
 Bayou Bodcau Crayfish
Bayou Bodcau Crayfish
 Bayou Homestead
Bayou Homestead
Bazooka [Musical Instrument]
 Bazooka
Bazooka
 Bazooka
Bazooka
 BBQ Sandwich
BBQ Sandwich
 Beach Scene
Beach Scene
Beacon of Peace and Hope
 Beaker Street Promo
Beaker Street Promo
 Bearden Plant Planer Mill
Bearden Plant Planer Mill
Bearden Waterworks
 Bearden Waterworks
Bearden Waterworks
 Beatles Sculpture at Walnut Ridge
Beatles Sculpture at Walnut Ridge
 Beaver Bridge
Beaver Bridge
 Beaver Bridge
Beaver Bridge
 Beaver Lake
Beaver Lake
 Beaver Lodges at Columbia Lake
Beaver Lodges at Columbia Lake




