 Conway-Crittenden Duel Story
Conway-Crittenden Duel Story
Entry Category: State
 Conway-Crittenden Duel Story
Conway-Crittenden Duel Story
Conway, Elias Nelson
Conway, James Sevier
Conway, Polly
aka: Mary Jane Bradley Conway
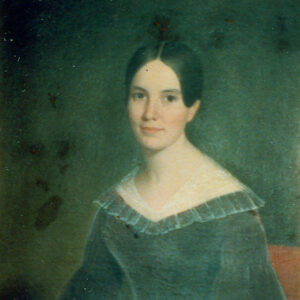 Polly Conway
Polly Conway
County Judge, Office of
Cox, David Adrian (Dave)
 Crank Campaign
Crank Campaign
 Crank Campaign Card
Crank Campaign Card
Crank, Marion Harland
 Crip Hall and Family
Crip Hall and Family
Crittenden, Robert
Cunningham, Charles E.
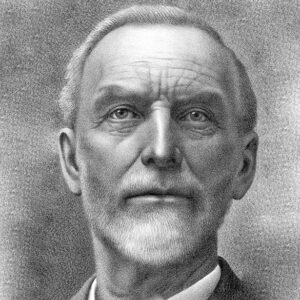 Charles E. Cunningham
Charles E. Cunningham
 Daniel Phillips Upham Death Story
Daniel Phillips Upham Death Story
 Daniels and Supporters
Daniels and Supporters
 Charlie Daniels
Charlie Daniels
Daniels, Charlie
Danley, Christopher Columbus
Darr, Mark
 Mark Darr
Mark Darr
 Dave Wallace
Dave Wallace
 Davis and Jackson
Davis and Jackson
 Davis Family
Davis Family
 Ina Davis
Ina Davis
 Jeff Davis Gravesite
Jeff Davis Gravesite
Davis, Jeff
 Jeff Davis Campaign
Jeff Davis Campaign
 Defending Moore
Defending Moore
Division of Elementary and Secondary Education
 Dome and Chandelier
Dome and Chandelier
Donaghey, George Washington
Drew, Thomas Stevenson
 W. R. Dyess
W. R. Dyess
Dyess, William Reynolds
 Eagle House
Eagle House
Eagle, James Philip
Eakin, Jno
aka: John Rogers Eakin
 Edmund Hogan Death Story
Edmund Hogan Death Story
 Elaine Massacre Aftermath
Elaine Massacre Aftermath
Elections during the Civil War
 Joyce Elliott
Joyce Elliott
Evans, Grover
 Grover Evans
Grover Evans
Famous and Historic Tree Program
 Farkle Finger
Farkle Finger
 Farkle Finger
Farkle Finger
Farkleberry Follies
 Faubus Bust
Faubus Bust
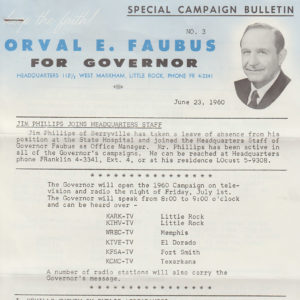 Faubus Newsletter
Faubus Newsletter




