Entry Category: Science and Technology - Starting with O
aka: Dragonflies
Official State Dinosaur
aka: Arkansas Dinosaur
aka: Arkansaurus fridayi
 Oil Trough Bridge
Oil Trough Bridge
 Old Main Street Bridge Demolition
Old Main Street Bridge Demolition
Opalinids
 Possum Show Article
Possum Show Article
Opossums
aka: Possums
aka: Didelphis virginiana
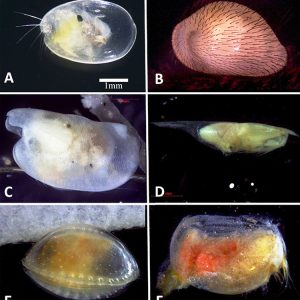 Ostracod Morphology
Ostracod Morphology
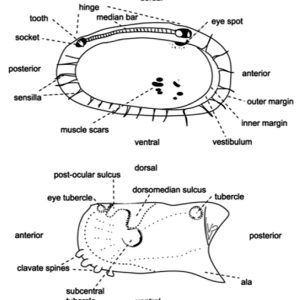 Ostracod Valve Features
Ostracod Valve Features
Ostracods
aka: Seed Shrimps
aka: Mussel Shrimps
 Ouachita Mountains Biological Station
Ouachita Mountains Biological Station
Ouachita Mountains Biological Station
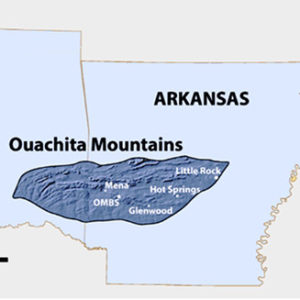 Ouachita Mountains Biological Station
Ouachita Mountains Biological Station
 Ouachita River
Ouachita River
 Ouachita Streambed Salamander
Ouachita Streambed Salamander




