 Lake Dick Kitchen
Lake Dick Kitchen
Entry Category: Projects
 Lake Dick Kitchen
Lake Dick Kitchen
 Lake Dick School and Community Center
Lake Dick School and Community Center
 Lakeview Children
Lakeview Children
 Lakeview Cooking Lesson
Lakeview Cooking Lesson
 Lakeview House
Lakeview House
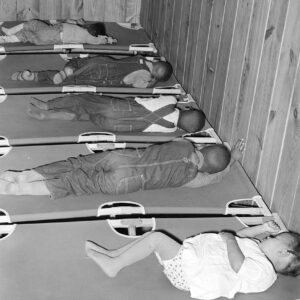 Lakeview Nursery
Lakeview Nursery
 Lakeview Students
Lakeview Students
 Lock and Dam No. 5
Lock and Dam No. 5
Louisiana Purchase
McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System (MKARNS)
 Murray Lock and Dam Overlook
Murray Lock and Dam Overlook
National Center for Toxicological Research (NCTR)
National Education Program
National Youth Administration
 Native American Emigration Story
Native American Emigration Story
 Native American Supplies Ad
Native American Supplies Ad
 Native American Treaty Story
Native American Treaty Story
New Deal
NYA Camp Bethune
aka: Camp Bethune
 NYA Camp Bethune Show Article
NYA Camp Bethune Show Article
Office of Removal and Subsistence
 Ordnance Plant Employee Manual
Ordnance Plant Employee Manual
 Ordnance Plant I.D. Badge
Ordnance Plant I.D. Badge
 Ordnance Plant Worker
Ordnance Plant Worker
 Piggott Post Office Art
Piggott Post Office Art
 Plum Bayou Buildings
Plum Bayou Buildings
Plum Bayou Project
Poland Committee
aka: Select Committee to Inquire into Conditions of the Affairs in the State of Arkansas
 Poland Committee Article
Poland Committee Article
Post Office Art
 Joseph Vorst's Post Office Mural
Joseph Vorst's Post Office Mural
Postage Stamps with Arkansas Connections
Public Works Administration
 Quarterboat
Quarterboat
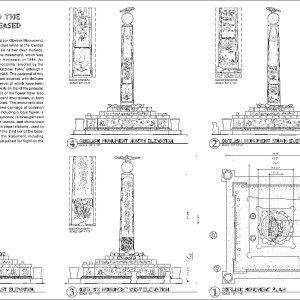 Rohwer Monument Plans
Rohwer Monument Plans
 Rohwer Outpost
Rohwer Outpost
Rohwer Relocation Center
 SEFOR Site
SEFOR Site
 Sharecropper House
Sharecropper House
Sharp, Willous Floyd
 Siloam Springs Post Office Art
Siloam Springs Post Office Art
Southwest Experimental Fast Oxide Reactor (SEFOR)
 John W. Sprague
John W. Sprague
 Thornburg CCC
Thornburg CCC
 Toad Suck Bridge
Toad Suck Bridge
 Toad Suck Ferry Lock and Dam No. 8
Toad Suck Ferry Lock and Dam No. 8
 Trail of Tears Sign
Trail of Tears Sign
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Little Rock District
 Van Buren Post Office Art
Van Buren Post Office Art
 Jamie Vogel
Jamie Vogel




