Entry Category: Military Science
Helena to Kent’s Landing, Expedition from
Helena to Mount Vernon, Scout from
Helena up the St. Francis River, Expedition from
Helena, Affairs at
Helena, Battle of
Helena, Expedition from (November 14–17, 1863)
Helena, Expeditions from (July 1862)
aka: Expedition from Helena to Marianna (July 24–26, 1862)
aka: Expedition from Helena to Old Town and Trenton (July 28–31, 1862)
Helena, Expeditions from (September 26, 1862)
aka: Expedition from Helena to Jeffersonville and Marianna
aka: Expedition from Helena to LaGrange
Helena, Skirmish at (September 19–20, 1862)
Helena, Skirmishes near (October 11, 1862)
aka: Battle of Jones's Lane
aka: Battle of Lick Creek
aka: Battle of Shell Creek
 Helicopter Crew
Helicopter Crew
 James R. Hendrix
James R. Hendrix
 James R. Hendrix Plaque
James R. Hendrix Plaque
Hendrix, James Richard
Herman Davis State Park
Herron, Francis Jay
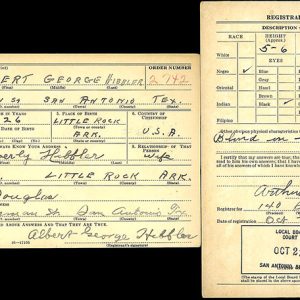 Hibbler Draft Card
Hibbler Draft Card
 D. O. Hickey
D. O. Hickey
Hickey, Doyle Overton
Hickory Plains, Skirmish at
Hickory Station, Skirmish at
 Daniel Harvey Hill
Daniel Harvey Hill
Hill, Daniel Harvey
Hill, Thomas Lionel
Hill’s Plantation, Action at
aka: Action at Cache River
aka: Action at Cotton Plant
aka: Action at Round Hill
Hindman, Thomas Carmichael
 Thomas Hindman's Residence
Thomas Hindman's Residence
Hodges, Jerry T.
Hollywood Cemetery—Confederate Section
aka: Hollywood Cemetery Confederate Section
 Hollywood Cemetery
Hollywood Cemetery
Holmes, Theophilus Hunter
Holt, George Moreau
Homer
 Homer Ad
Homer Ad
 Homer Shipwreck Site
Homer Shipwreck Site
Hopefield, Burning of
Horner, Elijah Whitt
Hospital Unit T
 Hospital Unit T Article
Hospital Unit T Article
 Hospital Unit T Paean
Hospital Unit T Paean
Hospitals (Civil War)
Hot Springs National Guard Armory
Hovey, Charles Edward
Howe, John David
 John G. Hudson
John G. Hudson
 John G. Hudson Death Notice
John G. Hudson Death Notice
Hudson, John Gardner
 William J. Hunter
William J. Hunter




