 Jones Poll Tax Receipt
Jones Poll Tax Receipt
Entry Category: Medicine
 Jones Poll Tax Receipt
Jones Poll Tax Receipt
 Jones Residence
Jones Residence
 Jones Speech
Jones Speech
 Edith Irby Jones
Edith Irby Jones
Jones, Edith Irby
 Edith Irby Jones
Edith Irby Jones
Jones, Fred Thomas
 Katie Chandler Jones
Katie Chandler Jones
 Jones's License
Jones's License
Jordan, Lena Lowe
Jordan, Wilbert Cornelius
 Orange King Judd
Orange King Judd
Kaplan, Regina
Keenan, Jimmie Owens
Kimbrough, Wilson Whitaker, Jr.
 Kissing Bug
Kissing Bug
Kountz, Samuel Lee, Jr.
Kumpuris, Michael Nicholas (Mike), Jr.
Lawrence Memorial Hospital
Lawrence, William M.
 William Lawrence
William Lawrence
 William Lawrence Grave
William Lawrence Grave
 Lee County Cooperative Clinic
Lee County Cooperative Clinic
Levi Hospital
aka: Leo N. Levi Hospital
Lowe, Betty Ann
Malaria
Malaria Control Projects in Southeast Arkansas
Malnutrition
 Marylake Monastery
Marylake Monastery
Maternal and Infant Mortality
Mayfield, Mary Victor (M. V.)
 Mays, Roberts, Trickey
Mays, Roberts, Trickey
 John McAlmont
John McAlmont
McAlmont, John Josephus
McDonald, Harry Pelot
McQuany, Joseph Daniel
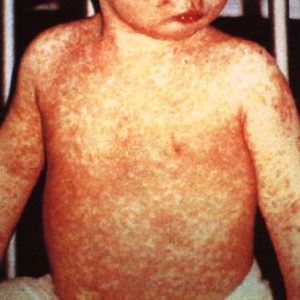 Measles Rash
Measles Rash
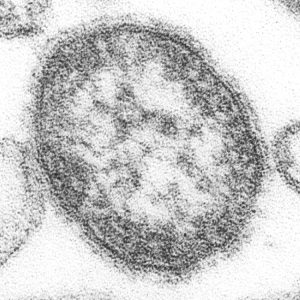 Measles Virus
Measles Virus
Medical Arts Building
Medical Malpractice
Mental Health
Mental Health Council of Arkansas
 Harry M. Meyer
Harry M. Meyer
 Harry M. Meyer
Harry M. Meyer
Mickel, Lillian Estes Eichenberger
Midwives
 Missouri Pacific Hospital
Missouri Pacific Hospital
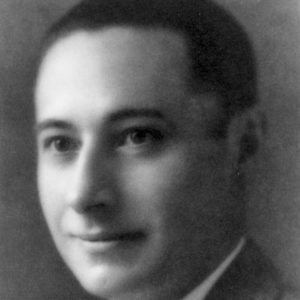 Robert Booth Moore
Robert Booth Moore
Morris, John William
 NPCC Dierks Building
NPCC Dierks Building




