Entry Category: Events
Benton, Skirmish at (December 1, 1863)
Benton, Skirmish at (July 6, 1864)
Bentonville, Action at
Bentonville, Skirmish at
Berryville Expedition
aka: Carrollton Expedition
aka: Huntsville Expedition
Berryville, Reconnaissance to (March 3–7, 1862)
Big Indian Creek, Skirmish at
aka: Skirmish at Big Creek
aka: Skirmish at Indian Creek
Big Lake Expedition
 Blue and Gray Reunion
Blue and Gray Reunion
Boggs’ Mills, Skirmish at
Branchville, Skirmish at
Brooks-Baxter War
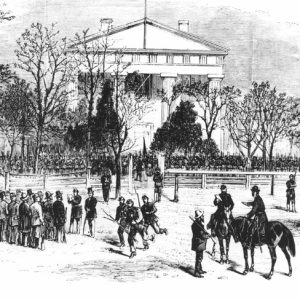 Brooks-Baxter War
Brooks-Baxter War
 Brooks-Baxter War Cannon
Brooks-Baxter War Cannon
 Brooks-Baxter War Cartoon
Brooks-Baxter War Cartoon
 Brownsville Skirmish
Brownsville Skirmish
Brownsville to Arkansas Post, Expedition from
Brownsville to Cotton Plant, Expedition from
Brownsville to Fairview, Expedition from
Brownsville, Scout from (January 17–19, 1864)
Brownsville, Scout from (June 27–29, 1864)
Brownsville, Skirmish at (August 25, 1863)
Brownsville, Skirmish at (July 13–14, 1864)
Buck Horn, Skirmish at
Buckskull, Skirmish at (November 20, 1864)
Buckskull, Skirmishes at (October 1 and 10, 1863)
Buffalo Mountains, Skirmish at
Buffalo River Expedition
 Napoleon Buford
Napoleon Buford
Bull Bayou, Skirmish at
Burrowsville, Skirmish at
aka: Skirmish at Tomahawk
 C-130 Crash
C-130 Crash
C-130 Crash of 1970
C-130 Crash of 1971
Cache Bayou, Skirmish at
Cache River Bridge, Skirmish at
Caddo Mill, Skirmish at
 Camden Vets
Camden Vets
Camden Expedition
Camden, Skirmish at (April 15, 1864)
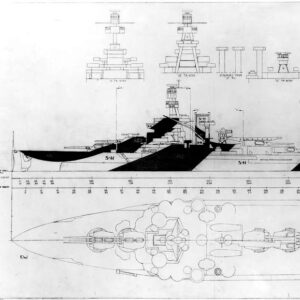 Camouflage Scheme
Camouflage Scheme
 Camp Shaver
Camp Shaver




