Entry Category: Education
 Everton School Detail
Everton School Detail
Evolution, Teaching of
 Faculty Row
Faculty Row
Fair View School
Far West Seminary
 Far West Seminary Story
Far West Seminary Story
 Far West Seminary Story
Far West Seminary Story
Fargo Agricultural School
 Fargo Agricultural School Ruins
Fargo Agricultural School Ruins
 Fargo Basketball Team
Fargo Basketball Team
 Fargo Football Team
Fargo Football Team
 Fargo Girls Chorus
Fargo Girls Chorus
 Fargo Girls Dorm
Fargo Girls Dorm
 Fargo School Girls
Fargo School Girls
 Fargo School Sign
Fargo School Sign
 Fargo School Students
Fargo School Students
 Fargo Sewing Class
Fargo Sewing Class
Fayetteville Female Seminary
 Fayetteville Female Seminary Report Card
Fayetteville Female Seminary Report Card
Fayetteville Schools, Desegregation of
 Stewart Ferguson
Stewart Ferguson
 Fine Arts Building
Fine Arts Building
Fishback School
 Fishback School
Fishback School
 Fishback School
Fishback School
 Isaac Fisher
Isaac Fisher
Fisher, Isaac
 Isaac Fisher in Africa
Isaac Fisher in Africa
 Isaac Fisher Letter
Isaac Fisher Letter
 Fletcher Library
Fletcher Library
 Adolphine Krause Fletcher
Adolphine Krause Fletcher
Flowers, Beulah Lee Sampson
 Fones Brothers Building
Fones Brothers Building
 Fones Brothers Building
Fones Brothers Building
 Fones Building
Fones Building
Ford, Archibald Washington (Arch)
 Fort Steele School
Fort Steele School
Foster, Jeannette Howard
 Lucretia Foster
Lucretia Foster
Freedmen’s Schools
Freedom Centers, Houses, Schools, and Libraries
 John Clinton Futrall
John Clinton Futrall
 John Clinton Futrall
John Clinton Futrall
Futrall, John Clinton
Galloway Women’s College
aka: Galloway Female College
 Galloway Women's College
Galloway Women's College
Garland County Public Library
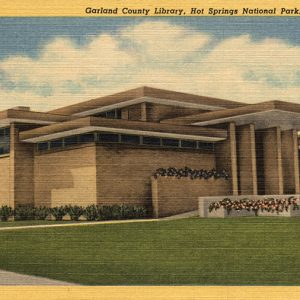 Garland County Public Library
Garland County Public Library




