Entry Category: Defunct: Colleges and Universities
 Holiness College Story
Holiness College Story
Jonesboro Baptist College
Judson University
 Judson University Assistance Story
Judson University Assistance Story
 KKK Donation
KKK Donation
LaCrosse Collegiate Institute
Little Rock College
 Little Rock College Postcard
Little Rock College Postcard
 Little Rock University
Little Rock University
 Little Rock University
Little Rock University
Little Rock University
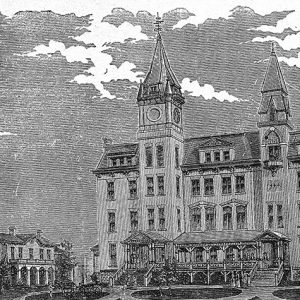 Little Rock University
Little Rock University
Makemie College
 Matthews Hall
Matthews Hall
Missionary Baptist College
Morrilton Male and Female College
 Morris Hall
Morris Hall
Mountain Home (Baptist) College
 Kate Richards O'Hare
Kate Richards O'Hare
 Opening Preparations
Opening Preparations
Ozark Industrial College and School of Theology
Pea Ridge Academy
aka: Mount Vernon Normal College
aka: Mount Vernon Masonic College
aka: Pea Ridge Normal College
 Pea Ridge College Band
Pea Ridge College Band
Phi Kappa Sigma Male College
 Albert Pike House
Albert Pike House
Quitman Male and Female College
 Richard Allen Institute Ad
Richard Allen Institute Ad
 Richard Allen Institute Fire Story
Richard Allen Institute Fire Story
 Searcy College
Searcy College
Soulesbury Institute
aka: Soulesbury College
Southland College
Springdale College
 Springdale Commencement
Springdale Commencement
Springfield Male and Female Collegiate Institute
aka: Springfield College
St. Andrew’s College
St. John’s Seminary
St. Johns’ College
Stuttgart Training School
aka: Stuttgart College
aka: Stuttgart Normal School
Tulip Female Collegiate Seminary
aka: Ouachita Conference Female College
 Tulip Female Collegiate Seminary Ad
Tulip Female Collegiate Seminary Ad
 Tulip Female Collegiate Seminary Article
Tulip Female Collegiate Seminary Article




