 UA Football Team
UA Football Team
Entry Category: Campuses and Schools
 UA Football Team
UA Football Team
University of Central Arkansas (UCA)
University of the Ozarks
 Vandervoort School
Vandervoort School
 Vandervoort School
Vandervoort School
 Velvatex Ad
Velvatex Ad
Velvatex College of Beauty Culture
 Velvatex College of Beauty Culture
Velvatex College of Beauty Culture
 Vilonia School
Vilonia School
W. F. Branch High School
Waldron School Historic District
 Walker Center
Walker Center
 Walnut Grove School
Walnut Grove School
 Walton Fine Arts Center
Walton Fine Arts Center
 Wandering Weevils
Wandering Weevils
 Wells Hall
Wells Hall
 White County Training School
White County Training School
Williams Baptist University
 Williford School
Williford School
Winchester School for Mountain Boys
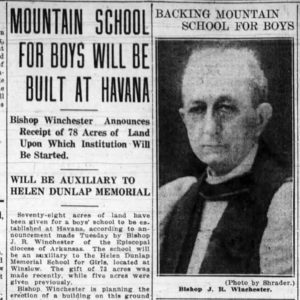 Winchester School Opening
Winchester School Opening
Wing School
 Winslow School
Winslow School
Winthrop School Museum
 Winthrop School Museum Exhibit
Winthrop School Museum Exhibit
 Winthrop School Construction
Winthrop School Construction
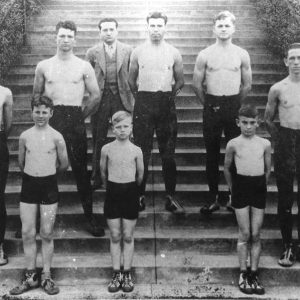 Wrestlers at School for the Deaf
Wrestlers at School for the Deaf




