 Antimony City Article
Antimony City Article
County: Sevier
 Antimony City Article
Antimony City Article
 Antimony Mining Article
Antimony Mining Article
 Archer Hospital
Archer Hospital
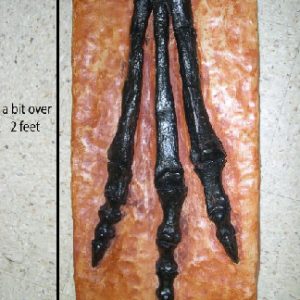 "Arkansaurus fridayi"
"Arkansaurus fridayi"
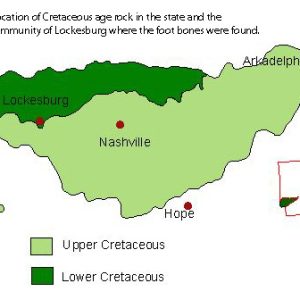 Arkansaurus fridayi Territory Map
Arkansaurus fridayi Territory Map
 Henry Atchley House
Henry Atchley House
Ben Lomond (Sevier County)
Bishop Brookes House
 Bishop Brookes House
Bishop Brookes House
brigham, besmilr moore
aka: Bess Miller Moore
 Choctaw Nation Border Marker
Choctaw Nation Border Marker
Cossatot Community College of the University of Arkansas (CCCUA)
 Cossatot River Bridge
Cossatot River Bridge
 Davis Mine
Davis Mine
De Queen (Sevier County)
 De Queen Chamber of Commerce
De Queen Chamber of Commerce
 De Queen and Eastern Railroad Machine Shop
De Queen and Eastern Railroad Machine Shop
De Queen Bee
 De Queen Bee
De Queen Bee
 De Queen Commercial Historic District
De Queen Commercial Historic District
De Queen Commercial Historic District
 De Queen Depot
De Queen Depot
 De Queen Fire Department
De Queen Fire Department
 De Queen Hotel
De Queen Hotel
 De Queen Post Office Art
De Queen Post Office Art
 De Queen School
De Queen School
 De Queen Street Scene
De Queen Street Scene
 De Queen Street Scene
De Queen Street Scene
 Dierks Mill
Dierks Mill
 Fort Towson Trail Marker
Fort Towson Trail Marker
Gillham (Sevier County)
Gillham City Jail
 Gillham City Jail
Gillham City Jail
Graves, Levi (Lynching of)
 Levi Graves Lynching Article
Levi Graves Lynching Article
 Hale Creek Bridge
Hale Creek Bridge
Hale Creek Bridge
 Horatio Peach Harvesters
Horatio Peach Harvesters
Horatio (Sevier County)
 Horatio Post Office
Horatio Post Office
 Horatio Theater
Horatio Theater
Jefferies, Oscar (Lynching of)
 Jefferies Lynching Article
Jefferies Lynching Article
Johnson, Cecil Ernest
King Schoolhouse
 King Schoolhouse
King Schoolhouse
 Lion Oil Pump House
Lion Oil Pump House
 "Little Rock," Performed by Collin Raye
"Little Rock," Performed by Collin Raye
Lockesburg (Sevier County)
 Little Cossatot River Bridge
Little Cossatot River Bridge




