Time Period: Louisiana Purchase through Early Statehood (1803 - 1860)
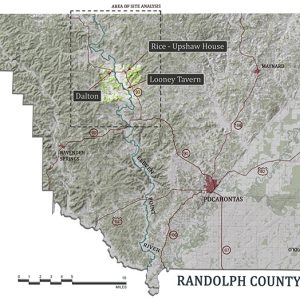 Randolph County Sites
Randolph County Sites
 John Randolph
John Randolph
Randolph, Meriwether Lewis
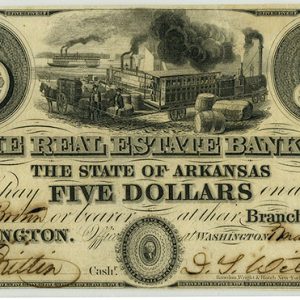 Real Estate Bank Note, 1840
Real Estate Bank Note, 1840
Rector, Elias
 Georgie Reddin
Georgie Reddin
 Rescue by Sarasin
Rescue by Sarasin
 Casper Reutzel House
Casper Reutzel House
Rice-Upshaw House
 J. R. Ridge Article
J. R. Ridge Article
Ridge, John Rollin
 Sarah Bird Northrup Ridge
Sarah Bird Northrup Ridge
Ridge, Sarah Bird Northrup
Ringo, Daniel
 John Roane
John Roane
Roane, John Selden
Rob Roy [Steamboat]
Rockport Cemetery
 Rose Statue
Rose Statue
 Uriah Milton Rose
Uriah Milton Rose
Rosedale Plantation Barn
 John Ross
John Ross
Ross, Quatie
 Quatie Ross Tombstone
Quatie Ross Tombstone
 Rosston Segment
Rosston Segment
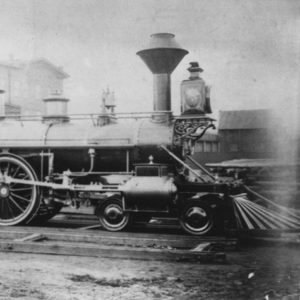 Roswell Beebe Locomotive
Roswell Beebe Locomotive
Rowland-Lenz House
 Grandison Royston
Grandison Royston
Royston, Grandison Delaney
 Runaway Slave Article
Runaway Slave Article
 Albert Rust Speech
Albert Rust Speech
Rust, Albert
Sager, Simon
 Simon Sager
Simon Sager
 Saladin Article
Saladin Article
 Salt Kettle
Salt Kettle
Sarah Bird Northrup Ridge House
Sarasin
aka: Saracen
aka: Sarrasin
aka: Sarasen
 Sarasin's Tombstone
Sarasin's Tombstone
 Sawdust Bridge Sign
Sawdust Bridge Sign
 Sophia Sawyer
Sophia Sawyer
Sawyer, Sophia
 Henry Schoolcraft
Henry Schoolcraft
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe
Scott County Lynching of 1843
Scott-Selden Duel
aka: Selden-Scott Duel
 Andrew Scott
Andrew Scott




