Time Period: Louisiana Purchase through Early Statehood (1803 - 1860) - Starting with C
aka: Cadron (Faulkner County)
 Cadron Settlement Marker
Cadron Settlement Marker
 John Calhoun
John Calhoun
California Gold Rush, Effect of the
Camden to Washington Road, Rosston Segment
Campbell Cemetery
Cane Hill College
Cane Hill Murders of 1839
Captain Isaac N. Deadrick House
Car of Commerce [Steamboat]
 Carnall Obituary
Carnall Obituary
Carnall, John
Caroline [Steamboat]
 Caroline Steamboat Article
Caroline Steamboat Article
 Caroline Steamboat Article
Caroline Steamboat Article
 Caroline Steamboat Article
Caroline Steamboat Article
Carrollton Road
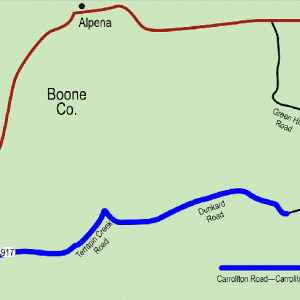 Carrollton Road
Carrollton Road
 Case-Shiras-Dearmore House
Case-Shiras-Dearmore House
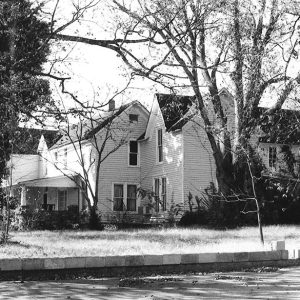 Case-Shiras-Dearmore House
Case-Shiras-Dearmore House
 Casey House
Casey House
 Casey House
Casey House
Casey House
 Cathedral of St. Andrew
Cathedral of St. Andrew
Cattle Drives
Caulder, Peter
Cherokee [Steamboat]
Cherokee Boundary Line
aka: Old Cherokee Boundary Line
 Chicot County Lynching Article
Chicot County Lynching Article
Chicot County Lynching of 1836
aka: Bunch (Lynching of)
Choctaw Boundary Line
 Choctaw Boundary Line
Choctaw Boundary Line
Choctaw Scrip
Cholera
Circuit Riders
 William Clark
William Clark
Clarksville [Steamboat]
 Henry Clay
Henry Clay
Clendenin, John J.
Clermont No. 2 [Steamboat]
 Clermont Steamboat Article
Clermont Steamboat Article
 Clermont Steamboat Article
Clermont Steamboat Article
Collins, Richard D’Cantillon
 Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
 Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
Collision of Congress and Saladin Article
Columbia (Chicot County)
 Columbia County Courthouse
Columbia County Courthouse
Comet [Steamboat]
 Comet Article
Comet Article
 Lee Compere
Lee Compere




