 Union Hill School
Union Hill School
Entry Type: Group
 Union Hill School
Union Hill School
Union Labor Party
Unionists
Unitarian Universalists
United Confederate Veterans (UCV)
 UDC Banquet
UDC Banquet
United Daughters of the Confederacy
 United Harmonizers
United Harmonizers
United Mine Workers of America (UMWA)
United Sons of Ham of America
aka: Sons of Ham
United States Representatives from Arkansas
United States Senators from Arkansas
Universal Negro Improvement Association (UNIA)
 UAMS Students; 1908
UAMS Students; 1908
 UA Football Team
UA Football Team
Urban League
 USS Razorback Crew
USS Razorback Crew
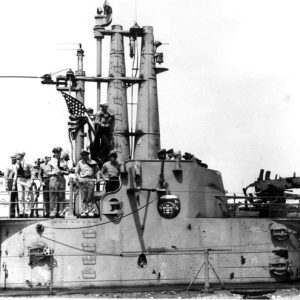 USS Razorback Officers and Crew
USS Razorback Officers and Crew
Van Buren County Historical Society
 Van Buren Desegregation
Van Buren Desegregation
Vera Lloyd Presbyterian Family Services
Village Academy Beavers
 The Vipers
The Vipers
Volunteers in Service to America (VISTA)
aka: VISTA
 W. H. Allen House in 1904
W. H. Allen House in 1904
 William J. Waggoner and Ruth Bradford
William J. Waggoner and Ruth Bradford
 Walnut Ridge Army Flying School
Walnut Ridge Army Flying School
 Walnut Ridge Baseball Club
Walnut Ridge Baseball Club
 Lon Warneke
Lon Warneke
 Joyce Warren at Governor's Mansion
Joyce Warren at Governor's Mansion
 Joyce Warren at Supreme Court
Joyce Warren at Supreme Court
Washington County Historical Society
 WCTU Banquet
WCTU Banquet
 WCTU Float
WCTU Float
 Webb House Restoration Workshop
Webb House Restoration Workshop
Weekend Theater
WEHCO Media, Inc.
 West and Henson
West and Henson
 West Family
West Family
 West Memphis Three
West Memphis Three
 West Memphis Three Victims
West Memphis Three Victims
West Memphis Three
 Westbrook Testimonial Dinner
Westbrook Testimonial Dinner
 Wetland Planning
Wetland Planning
Whig Party
White County Historical Society
White Revolution
 Elton and Betty White
Elton and Betty White
 George Bush with Gay and Frank White
George Bush with Gay and Frank White
 Wilburn Brothers' Back in Town
Wilburn Brothers' Back in Town




