Entry Category: Military Science
Smith, Edmund Kirby
Smith, Sarah Jane
 William Y. Smith
William Y. Smith
Smith, William Young
Smithville, Skirmish at (June 17, 1862)
 William Anderson Snodgrass
William Anderson Snodgrass
 Brehon Burke Somervell
Brehon Burke Somervell
Somervell, Brehon Burke
Southern Missouri and Northern Arkansas Expedition
 Southwest Proving Ground
Southwest Proving Ground
Spanish-American War
 Spanish-American War Memorial
Spanish-American War Memorial
Spavinaw, Skirmish at
Spirit of the American Doughboy Monuments
 Sprague Memorial
Sprague Memorial
Sprague, Charles Leslie
Sprague, John Wilson
Spring River near Smithville, Skirmish at
aka: Skirmish at Spring River (April 13, 1864)
aka: Skirmish at Smithville (April 13, 1864)
Spring River, Action at
aka: Battle of Salem
Springfield, Missouri, into Northern Arkansas, Scout from
aka: Skirmish at Bennett’s Bayou
aka: Skirmish near Buffalo City
Springfield, Missouri, toward Fayetteville, Scout from
SS Ouachita Victory
 St. Charles Battle Monument
St. Charles Battle Monument
St. Charles, Capture of
St. Charles, Engagement at
St. Francis Road, Skirmish at
 Skirmish at Tomahawk
Skirmish at Tomahawk
Steamboats (Civil War)
Steamer Alamo, Attack on
Steamer Miller, Capture of
Steamer Perry, Attack on
Steamer Resolute, Attack on
Steele, Frederick
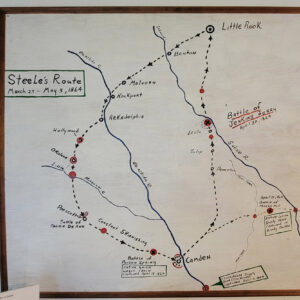 Steele's Routes
Steele's Routes
 Steiner Grave
Steiner Grave
Steiner, Christian
 Roger Nelson Stembel
Roger Nelson Stembel
 N. W. Stewart
N. W. Stewart
Stewart’s Plantation, Skirmish at
Stirman, Erasmus Irving
 James L. Stone
James L. Stone
 James L. Stone
James L. Stone
 James L. Stone Plaque
James L. Stone Plaque
Stone, James Lamar
 Cornelius Stribling
Cornelius Stribling




